Gum Inflammation and Gingivitis Case Analysis With Healing Timeline
Teeth Case – Full Analysis and Provisional Diagnosis (Zoom 100%)
This assessment is based on a photographic image only. A definitive diagnosis requires an in-person dental examination, periodontal probing, and radiographs when indicated.
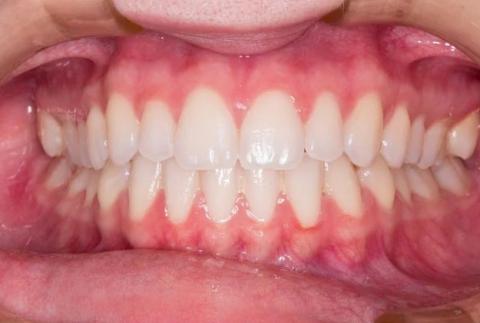
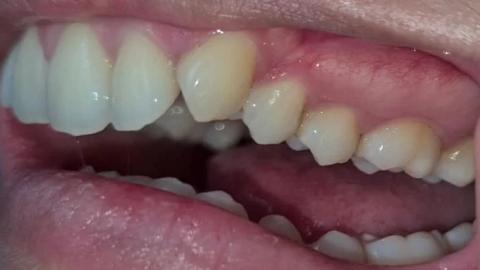
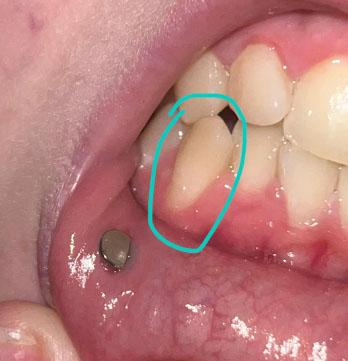
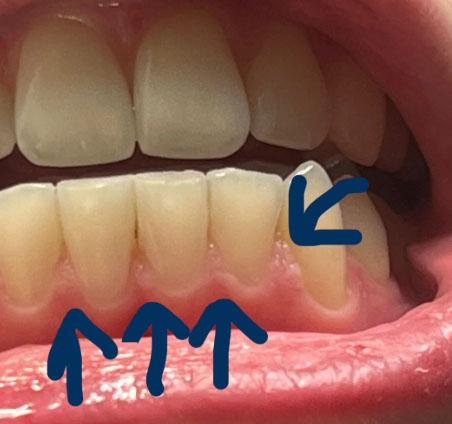
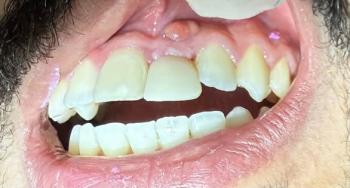
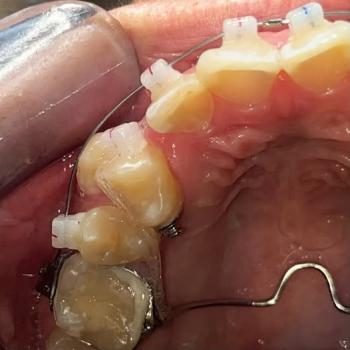
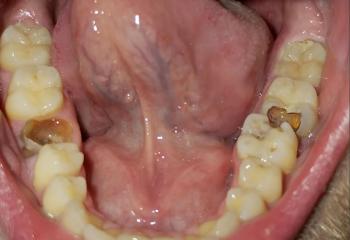
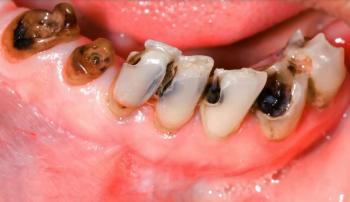
1. Visual Findings (Deep Examination)
-
Teeth alignment and surfaces:
-
Teeth appear generally well-aligned with smooth enamel surfaces.
-
No obvious cavities, fractures, or restorations visible in this image.
-