Transforming Smiles, Restoring Confidence.
Localized Gum Recession on Premolar | Causes, Treatment, and Prevention
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
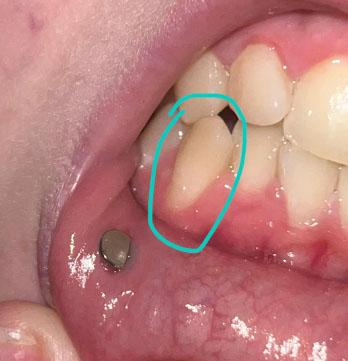
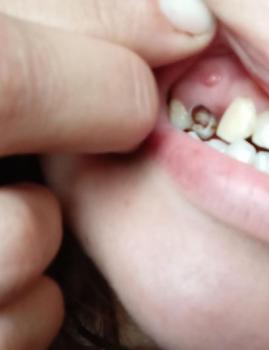
ocalized Gum Recession and Root Exposure on Lower Premolar – Full Dental Case Analysis (100% Zoom)
Medical Disclaimer
This analysis is image-based and for educational purposes only. A definitive diagnosis requires an in-person dental examination, periodontal probing, and dental X-rays. The findings below are based on visible clinical signs and accepted dental standards.
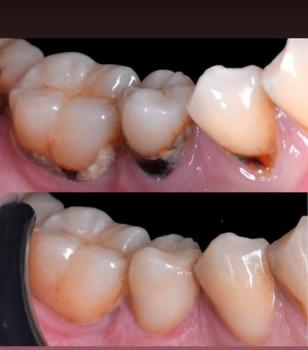
Case Overview (Zoom 100%)
The circled tooth shows localized gum recession on a lower premolar, with visible root surface exposure. The gum margin has migrated downward, exposing the lighter-colored root area compared to the enamel above. The surrounding gum tissue appears mildly inflamed but without obvious pus or acute infection.
A metal stud visible on the lip is unrelated to the dental condition.
This presentation is consistent with early-to-moderate gingival recession, not active tooth decay.
Primary Diagnosis
-
Localized gingival recession on a lower premolar
-
Exposed root surface (cementum/dentin exposure)
-
Early non-carious cervical lesion risk
-
Increased susceptibility to tooth sensitivity and root caries
Deep Clinical Examination (Image-Based Findings)
-
Gum margin positioned apical to its normal level
-
Smooth, light-colored exposed root surface
-
Mild gingival inflammation at the recession margin
-
No visible abscess, ulceration, or necrotic tissue
-
Likely contributing factors:
-
Aggressive or improper brushing technique
-
Thin gum biotype
-
Local plaque accumulation
-
Occlusal stress or tooth position
-
Can This Heal in 14 Days?
Gum recession does not reverse naturally.
However, within 14 days, appropriate dental care can:
-
Stop further recession
-
Reduce inflammation
-
Decrease or prevent sensitivity
-
Protect the exposed root surface
Early management is key to long-term stability.
Recommended Treatment Process
Step 1: Periodontal Assessment (Days 1–3)
-
Periodontal probing to measure recession depth
-
Evaluation of gum thickness and attachment level
-
Assessment of brushing habits and bite forces
Step 2: Disease Control and Prevention (Days 3–7)
-
Professional scaling and polishing
-
Removal of plaque near the gum line
-
Instruction on gentle brushing technique
-
Use of desensitizing toothpaste if sensitivity exists
Step 3: Protective or Corrective Care (Days 7–14)
Depending on severity and symptoms:
-
Fluoride or desensitizing varnish
-
Cervical composite restoration if root wear progresses
-
Occlusal adjustment if traumatic bite is present
-
Periodontal referral if recession continues to worsen
Expected Healing Timeline
-
Reduction in gum inflammation: 7–10 days
-
Sensitivity improvement: 1–2 weeks
-
Long-term stabilization depends on habit correction and maintenance
Note: Gum tissue will stabilize but will not regrow without surgical intervention.
What Will Escalate If Untreated
-
Increased tooth sensitivity
-
Higher risk of root caries
-
Progressive gum recession
-
Aesthetic concerns due to elongated tooth appearance
-
Potential future tooth mobility in advanced cases
Professional Comments
This is a common and manageable dental condition. When addressed early, most patients maintain their teeth long-term without surgery. The key is early prevention and habit correction, not aggressive treatment.
This is not an emergency, but it should not be ignored.
Strong Recommendation
Schedule a dental visit for periodontal evaluation and preventive treatment.
You can find a dental clinic near your area using this directory:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic
Early care prevents more complex and costly procedures later.