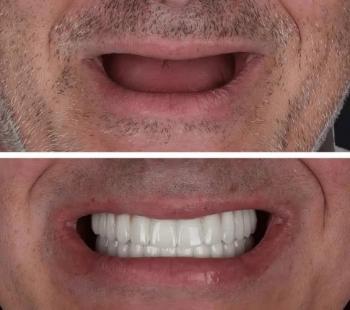
Missing Teeth? Find Your Smile Again.
Severe Tooth Decay With Gum Infection - Dental Case Analysis
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
Dental Case Analysis – Severe Tooth Decay With Localized Gum Infection
Case Overview
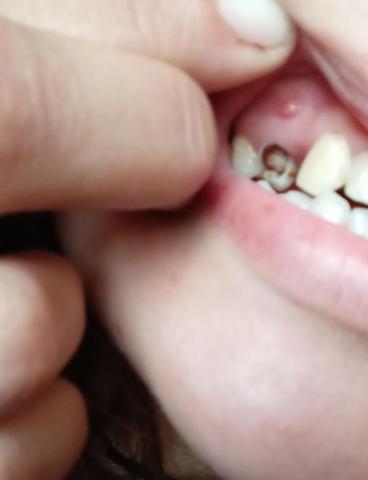
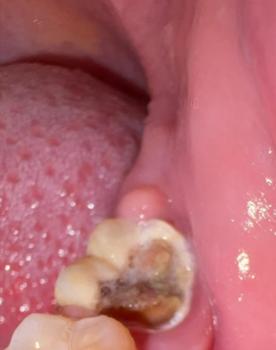
This intra-oral image shows a tooth with advanced decay and an associated localized gum swelling above the affected tooth. The appearance suggests an active dental infection likely originating from deep caries that has reached the pulp and spread toward the surrounding soft tissue.
Full Analysis and Diagnosis
Clinical Findings
-
Deep cavity with visible tooth structure breakdown
-
Darkened, decayed area inside the tooth
-
Red, raised gum swelling above the affected tooth
-
Signs of localized inflammation
-
Adjacent teeth appear relatively intact
Infection Characteristics
-
Bacterial invasion of the pulp chamber
-
Infection tracking toward the gum tissue
-
Possible formation of a draining sinus or abscess
-
Infection pressure localized but active
Diagnosis
-
Advanced dental caries
-
Apical or periodontal abscess
-
Localized odontogenic infection
Deep Clinical Examination
Tooth Assessment
-
Pulp involvement is highly likely
-
Tooth vitality compromised
-
Structural integrity weakened
-
High risk of pain flare-ups
Gum and Bone Assessment
-
Soft tissue inflammation present
-
Possible early bone involvement
-
Infection may extend if untreated
Time Frame to Heal
With Proper Treatment
-
Infection control: 5–7 days
-
Swelling reduction: 7–10 days
-
Soft tissue healing: 1–2 weeks
-
Bone recovery (if affected): 4–8 weeks
Without Treatment
-
Abscess enlargement
-
Increased pain and swelling
-
Spread of infection to jawbone
-
Facial swelling
-
Risk of systemic infection
-
Tooth loss
Process to Execute (14-Day Window)
Days 1–3
-
Clinical examination
-
X-ray or CBCT if required
-
Drainage if abscess is present
-
Antibiotics only if clinically indicated
Days 4–7
-
Definitive treatment decision
-
Root canal treatment or
-
Tooth extraction if non-restorable
-
-
Local infection control
Days 8–14
-
Follow-up assessment
-
Monitor healing of gum tissue
-
Plan long-term restoration or space management
Issues That Will Scale Up If Untreated
-
Rapid abscess progression
-
Jawbone infection
-
Facial cellulitis
-
Fever and systemic spread
-
Emergency hospitalization in severe cases
-
Permanent damage to developing teeth (if pediatric)
Clinical Comments
Deep cavities with associated gum swelling indicate that infection has moved beyond the tooth surface. These cases should be treated promptly to prevent pain escalation and serious complications. Early intervention significantly improves outcomes.
Find a Dental Clinic Near You
Locate a qualified dental clinic using our directory:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic