Building Confidence One Smile at a Time.
Deep Cavity on Back Molar With Early Gum Infection
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
Deep Cavity on Back Molar With Early Gum Infection Case Analysis
What Is Seen in This Case
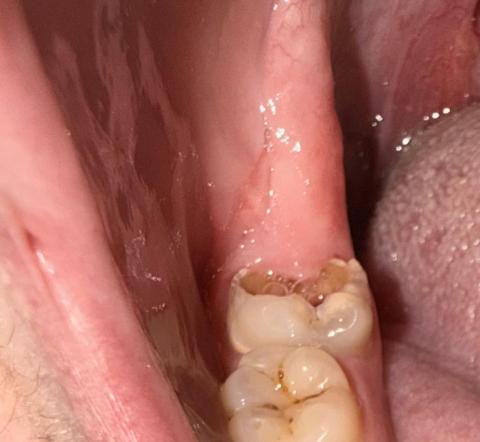
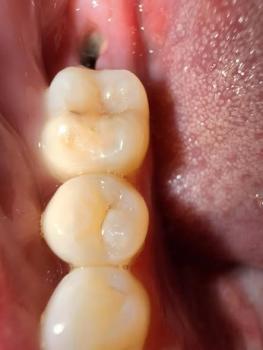
The image shows a back molar with a deep cavity on the chewing surface, where the enamel has broken down and darker material is visible inside the tooth. The gum tissue beside the tooth looks irritated and slightly inflamed, suggesting early gum infection next to an actively decaying molar. The tongue is close to the area, which may increase discomfort.
This type of cavity is often painful and can worsen quickly if untreated.
Most Likely Diagnosis
Based on visual examination, the most likely conditions include:
-
Deep dental caries (advanced cavity)
-
Early gum infection adjacent to the molar
-
High risk of pulp (nerve) infection
-
Possible early tooth abscess formation
-
Food and bacteria retention in the cavity
A dental X-ray is needed to confirm whether the decay has reached the tooth nerve.
What Causes This Type of Tooth and Gum Problem
Common causes include:
-
Long-standing untreated cavity
-
Frequent sugary or acidic food intake
-
Incomplete brushing of back teeth
-
Deep grooves on molars that trap bacteria
-
Delayed dental visits
Back molars are especially prone to deep decay because they are harder to clean.
Is This a Serious Problem
Yes. This is an active and progressing condition. If left untreated, it may scale up into:
-
Severe toothache
-
Tooth nerve infection
-
Gum abscess or pus formation
-
Jawbone infection
-
Tooth fracture or loss
Early treatment can often save the tooth.
Recommended Treatment Process
Initial Assessment (Days 1–3)
-
Dental examination
-
Dental X-ray to assess decay depth
-
Evaluation of gum and bone involvement
Active Treatment Phase (Days 4–7)
Treatment may include:
-
Dental filling if decay has not reached the nerve
-
Root canal treatment if the nerve is infected
-
Deep cleaning of the gum area
-
Antibiotics if signs of infection are present
Healing and Follow-Up Phase (Days 8–14)
-
Pain and sensitivity should reduce
-
Gum inflammation improves
-
Tooth function stabilizes
Further restorative treatment may be planned if needed.
Expected Healing Time
-
After filling: 1–3 days
-
After root canal: 5–10 days
-
Gum healing: 7–14 days
Healing depends on how advanced the decay is.
What Happens If Treatment Is Delayed
Delaying care may lead to:
-
Rapid spread of infection
-
Tooth abscess formation
-
Bone loss around the molar
-
Emergency dental treatment
-
Higher risk of tooth extraction
This condition will not improve on its own.
Home Care While Waiting for Treatment
These steps may help reduce discomfort but do not stop decay:
-
Rinse with warm salt water
-
Brush gently around the tooth
-
Avoid chewing on the affected side
-
Avoid sugary and sticky foods
Dental treatment is still required.
Professional Comment
This case shows a deep cavity on a back molar with early gum infection, a common but serious problem. Early dental intervention can often prevent nerve damage and tooth loss.
Visit a Dental Clinic Near You
For professional evaluation and treatment, visit:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic