Strong Teeth, Fresh Breath, Brighter You.
Mouth Ulcer on Upper Lip – Dental Case Analysis
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
Dental Case Analysis – Painful Mouth Ulcer on Upper Lip
Case Overview
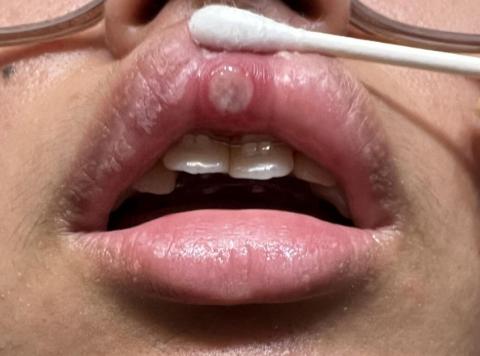
This image shows a round ulcerative lesion on the inner upper lip, with a white or pale center and surrounding red inflammation. The appearance is consistent with a localized oral ulcer, commonly associated with irritation, minor trauma, or immune response.
Scale All Teeth
-
Upper anterior teeth visible
-
Teeth appear intact and aligned
-
No visible decay or fractures in this image
-
Primary concern is soft tissue, not tooth structure
Full Analysis and Diagnosis
Clinical Findings
-
Single round ulcer on inner upper lip
-
White or grayish center
-
Red, inflamed border
-
Surrounding lip tissue appears dry and irritated
-
No visible pus or active bleeding
Interpretation
-
Findings are suggestive of an aphthous ulcer (mouth sore)
-
May be triggered by:
-
Minor trauma (biting, brushing)
-
Stress or fatigue
-
Nutritional deficiencies
-
Immune response
-
Irritation from dental appliances
-
Probable Diagnosis
-
Aphthous ulcer (canker sore)
-
Localized oral mucosal inflammation
(Clinical confirmation recommended.)
Deep Examination
Soft Tissue Assessment
-
Superficial mucosal breakdown
-
No signs of deep infection
-
Lesion appears localized
-
Pain likely present during eating or speaking
Risk Factors to Consider
-
Dry lips or mouth
-
Recent dental procedures
-
Orthodontic appliances
-
Acidic or spicy food intake
-
Stress-related immune changes
Time Frame to Heal
With Proper Care
-
Pain reduction: 2–4 days
-
Ulcer size reduction: 5–7 days
-
Complete healing: 7–14 days
Without Care
-
Prolonged pain
-
Delayed healing
-
Increased irritation
-
Possible secondary infection
-
Recurrent ulcer formation
Process to Execute (14-Day Window)
Days 1–3
-
Avoid spicy, acidic, and hard foods
-
Maintain gentle oral hygiene
-
Keep lips and mouth hydrated
Days 4–7
-
Monitor ulcer size and pain level
-
Reduce mechanical irritation
-
Maintain good nutrition
Days 8–14
-
Confirm ulcer resolution
-
Seek dental or medical evaluation if lesion persists
-
Investigate recurrent ulcer causes if applicable
Issues That Will Scale Up If Untreated
-
Persistent pain
-
Difficulty eating or speaking
-
Recurrent mouth ulcers
-
Secondary infection risk
-
Chronic mucosal irritation
Clinical Comments
Mouth ulcers are common and usually self-limiting, but persistent or recurrent sores should not be ignored. Lesions lasting longer than two weeks require professional evaluation to rule out underlying conditions.
Find a Dental Clinic Near You
Locate a dental clinic in your area using our directory:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic