Because Every Tooth Deserves Care.
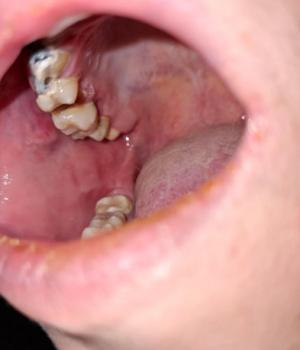
Painful Tongue Lesion Case Analysis and Healing Timeline
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
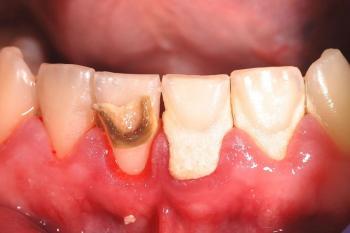
Teeth Case – Full Analysis and Provisional Diagnosis (Zoom 100%)
This assessment is based on visual inspection of the provided image only. A definitive diagnosis requires an in-person oral examination by a licensed dental or medical professional. Tongue lesions that persist or worsen must be clinically evaluated.
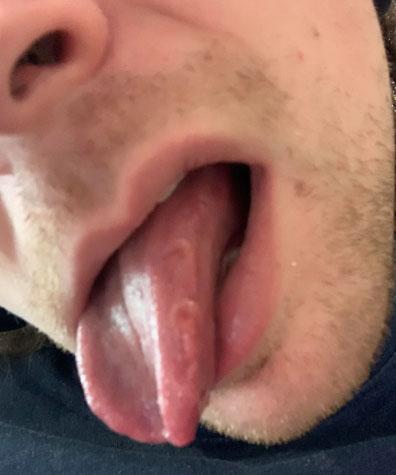
1. Visual Findings (Deep Examination)
-
Tongue (lateral and dorsal surface):
-
Visible linear fissure and localized circular lesions consistent with traumatic injury or irritation.
-
Surface appears mildly inflamed with areas of tenderness suggested by exposure and posture.
-
-
Surrounding oral tissues:
-
No obvious heavy swelling, but localized irritation is present.
-
-
Probable cause:
-
Repeated tongue biting, friction against sharp tooth edges, stress-related clenching, or accidental trauma.
-
-
Saliva and moisture:
-
Adequate saliva present, which supports healing if trauma is eliminated.
-
2. Most Likely Diagnosis (Provisional)
-
Traumatic tongue ulcer or fissure
-
Localized inflammatory tongue lesion
-
Repetitive mechanical irritation
3. Differential Diagnosis (If Lesion Persists)
-
Aphthous ulcer (canker sore)
-
Infected traumatic ulcer
-
Chronic irritation lesion
-
Less commonly, precancerous lesion if non-healing beyond 14 days
4. Recommended Treatment Process
Phase 1: Immediate Management (Days 1–3)
-
Identify and remove the cause of trauma (sharp tooth edge, fractured filling, or habitual biting).
-
Warm saline mouth rinses 2–3 times daily.
-
Topical protective oral gel or barrier paste as advised by a dentist.
-
Soft diet; avoid spicy, acidic, hot, or abrasive foods.
Phase 2: Healing Support (Days 4–7)
-
Maintain gentle oral hygiene.
-
Avoid alcohol and tobacco.
-
Use pain-relieving oral rinse if discomfort persists.
Phase 3: Re-evaluation (Days 8–14)
-
Lesion should significantly reduce in size and pain.
-
If no improvement or if pain worsens, immediate clinical evaluation is required.
Expected healing time:
-
Minor traumatic tongue injuries typically heal within 7–14 days once irritation stops.
5. If Healing Takes 14 Days – What May Scale Up
-
Persistent pain and ulceration
-
Secondary bacterial infection
-
Difficulty speaking, eating, or swallowing
-
Scar formation
-
Need for biopsy to rule out non-traumatic pathology
6. Home Care Recommendations (Interim)
-
Avoid repeated tongue movement against teeth.
-
Do not scrape, bite, or pick the lesion.
-
Stay hydrated.
-
Avoid very hot drinks.
7. Professional Commentary
Most tongue injuries are benign and heal rapidly when the source of trauma is removed. Any tongue lesion that does not heal within two weeks or shows growth, hardening, or bleeding must be examined promptly.
Visit Nearest Dental Clinic
Find a nearby dental clinic for proper oral examination and management:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic