Modern Dentistry, Timeless Smiles.
Anterior Teeth X-Ray Showing Bone Loss Case Analysis
Severity:
Anterior Teeth X-Ray Case Analysis and Bone Health Review
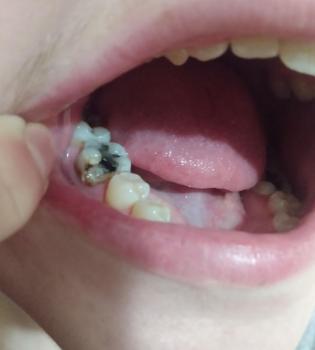
What Is Seen in This Case
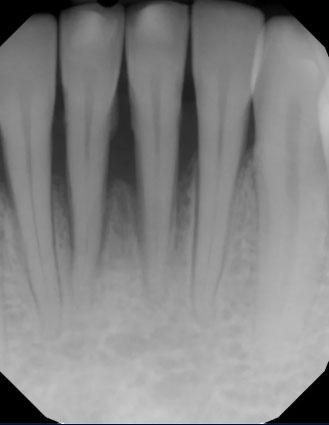
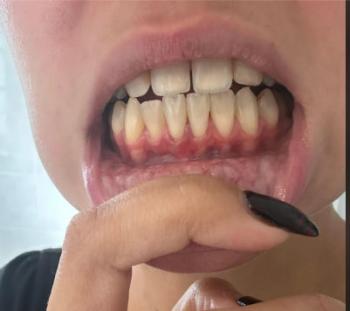
The dental X-ray shows the front teeth (anterior teeth) with clearly visible roots and surrounding bone. The bone level around the roots appears reduced and uneven, especially near the root tips. This finding can indicate early bone loss or a low-grade infection around one or more teeth.
There are no visible crowns or restorations in this area, which helps focus the evaluation on bone and root health.
Full Analysis and Provisional Diagnosis
Based on the X-ray appearance, the most likely findings include:
-
Early bone loss around anterior tooth roots
-
Possible chronic periapical infection
-
Reduced bone density near root tips
-
History of past trauma or infection
A clinical examination and symptom review are needed to determine whether the condition is active or stable.
What Causes Bone Changes Around Front Teeth
Common causes include:
-
Long-standing untreated infection
-
Past dental trauma to front teeth
-
Tooth nerve damage without symptoms
-
Gum disease affecting the bone
-
Delayed dental follow-up
Bone changes often progress silently and may not cause pain initially.
Is This a Serious Problem
This condition can become serious if left untreated. If ignored, it may scale up into:
-
Progressing bone loss
-
Tooth loosening
-
Abscess formation
-
Gum swelling near front teeth
-
Aesthetic and functional problems
-
Eventual tooth loss
Early diagnosis improves the chance of saving the teeth.
Recommended Treatment Process
Initial Assessment (Days 1–3)
-
Dental examination
-
Review of symptoms and history
-
Detailed X-ray evaluation
-
Comparison with previous images
Active Treatment Phase (Days 4–7)
Treatment may include:
-
Root canal treatment if nerve infection is confirmed
-
Monitoring if the area is healing and asymptomatic
-
Gum treatment if periodontal disease is present
Healing and Follow-Up (Days 8–14)
-
Monitor for pain, swelling, or changes
-
Plan follow-up X-rays
-
Reinforce oral hygiene and routine care
Expected Healing Time
-
Symptom improvement: 7–14 days
-
Bone healing: several months
-
Radiographic bone recovery requires long-term monitoring
Bone heals slowly and must be checked over time.
What Happens If Treatment Is Delayed
If delayed beyond 14 days or ignored long-term, the condition may worsen and lead to:
-
Increased bone destruction
-
Tooth instability
-
Chronic infection
-
Abscess development
-
Higher treatment cost
-
Tooth loss
Home Care While Under Observation
These steps support oral health but do not reverse bone loss:
-
Maintain excellent oral hygiene
-
Avoid biting hard objects with front teeth
-
Attend scheduled dental visits
-
Follow dentist recommendations carefully
Professional Comment
This X-ray highlights bone changes around anterior teeth, which often progress without pain. Early dental evaluation and monitoring are essential to protect both function and appearance.
Visit a Dental Clinic Near You
For professional X-ray review and treatment planning, visit:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic