Strong Teeth, Fresh Breath, Brighter You.
Jake Paul Mandibular Fracture and Dental Trauma Case - In-Depth Jaw and Teeth Injury Analysis
Language :

Teeth & Jaw Case Analysis (Zoom 100% – Clinical Perspective)
Case basis: Analysis is derived from the provided image set and the referenced news report. This is an educational discussion and not a substitute for an in-person clinical diagnosis.
1. Visual Findings (Scaled Dental & Jaw Assessment)
Extra-oral / Jaw
-
Evidence of mandibular fracture (lower jaw), likely involving the angle or body of the mandible
-
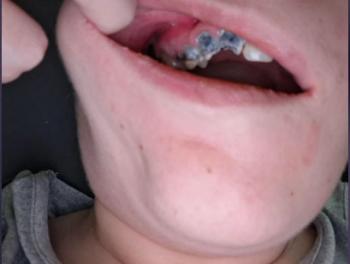
Facial swelling and soft-tissue trauma consistent with high-impact injury
-
Jaw instability suggested by fixation hardware visible in imaging
Intra-oral / Teeth
-
Dental displacement and trauma in the lower anterior/posterior region
-
Possible tooth subluxation or fracture, especially near the fracture line
-
Presence of blood and soft tissue laceration, indicating gingival and mucosal injury
-
Risk of occlusal misalignment (malocclusion) due to jaw fracture
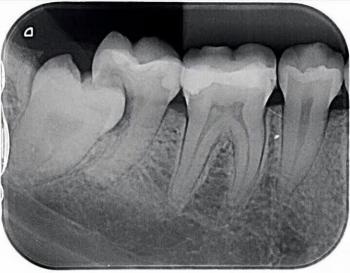
Radiographic (CT-style image shown)
-
Clear fracture line in the mandible
-
Fixation plate and screws indicate open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF)
-
Bone discontinuity with potential involvement of the inferior alveolar nerve canal
Diagnosis (Likely)
-
Mandibular fracture (moderate to severe)
-
Dental trauma secondary to jaw fracture
-
Soft tissue injury (gingiva, oral mucosa)
-
Possible nerve involvement (numbness of lower lip/chin)
-
High risk of infection if oral hygiene is compromised
Treatment Process Executed / Recommended
Acute Phase (Day 0–3)
-
Emergency stabilization
-
Imaging (CT scan / panoramic X-ray)
-
ORIF surgery with titanium plates and screws
-
Pain control and antibiotics
Early Healing Phase (Day 4–14)
-
Soft or liquid diet only
-
Strict oral hygiene with antiseptic rinses
-
Limited jaw movement
-
Monitoring for infection, swelling, or hardware failure
Dental Management
-
Stabilization of traumatized teeth
-
Delay definitive dental restorations until bone healing progresses
-
Vitality testing of affected teeth after 2–4 weeks
Healing Time Frame
-
Initial bone stability: ~2 weeks
-
Functional bone healing: 4–6 weeks
-
Complete bone remodeling: 3–6 months
-
Dental rehabilitation (if needed): after 8–12 weeks
If only 14 days of healing:
Bone is not fully healed. The fracture is still vulnerable to re-injury, infection, and malocclusion if stressed too early.
Issues That May Scale Up if Not Managed Properly
-
Chronic jaw pain or TMJ disorder
-
Permanent bite misalignment
-
Non-union or delayed union of the fracture
-
Tooth loss near the fracture site
-
Nerve damage causing long-term numbness
-
Infection around fixation hardware
-
Need for revision surgery
Clinical Comments
-
Jaw fractures with dental involvement require combined care from oral surgeons and restorative dentists
-
Early return to physical stress can reverse healing
-
Long-term success depends on diet compliance, oral hygiene, and follow-up imaging
-
Dental implants or crowns should only be planned after confirmed bone consolidation
Recommendation
If you or a patient experiences similar trauma symptoms:
-
Seek immediate oral and maxillofacial consultation
-
Do not ignore bite changes, numbness, or loose teeth
-
Early treatment significantly improves long-term outcomes
Visit Nearest Dental & Surgical Care
Find trusted dental and oral surgery clinics near you using our directory:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic
Early expert intervention can prevent complications and restore full function safely.
image source: https://www.geo.tv/latest/640521-jake-paul-suffers-broken-jaw-in-knockou...