Because Every Tooth Deserves Care.
Apical Infection After Root Canal - CBCT Dental Case
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
Dental Case Analysis – Apical Infection After Root Canal Treatment
Case Overview
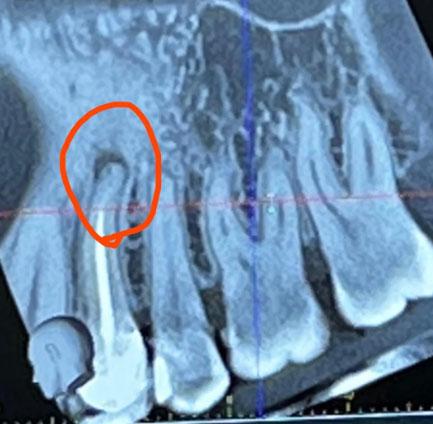
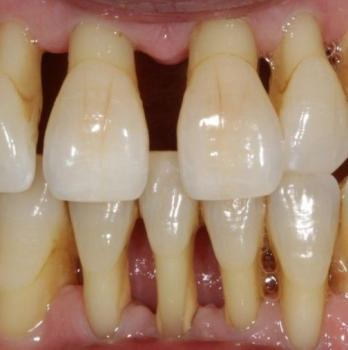
This CBCT image shows the anterior maxillary region with multiple natural teeth. A well-defined radiolucent lesion is visible at the root apex of a previously treated tooth (circled area), indicating a persistent apical infection. Surrounding bone shows early structural changes.
Full Analysis and Diagnosis
Radiographic Findings
-
Clear apical radiolucency at root tip
-
Loss of normal bone trabeculation
-
Root canal filling present but likely incomplete
-
Lesion confined but expanding
-
Adjacent teeth currently unaffected
Tooth Condition
-
Root canal–treated tooth
-
Possible missed canal or inadequate apical seal
-
Chronic low-grade infection
-
Tooth structure still salvageable
Diagnosis
-
Chronic apical periodontitis
-
Failed or compromised root canal treatment
-
Localized periapical bone loss
Deep Clinical Examination
Infection Characteristics
-
Long-standing infection rather than acute abscess
-
Minimal symptoms possible despite bone damage
-
Infection confined to apex but progressing
-
High risk of lesion enlargement if untreated
Bone Status
-
Early bone resorption visible
-
Cortical plate intact
-
Favorable prognosis if treated early
Time Frame to Heal
With Proper Treatment
-
Infection control: 7–14 days
-
Soft tissue recovery: 1–2 weeks
-
Bone healing begins: 4–6 weeks
-
Radiographic improvement: 3–6 months
Without Treatment
-
Lesion enlargement
-
Progressive bone destruction
-
Pain, swelling, or abscess
-
Eventual tooth loss
Process to Execute (14-Day Focus)
Days 1–3
-
Clinical evaluation and CBCT review
-
Confirm infection source
-
Decide between retreatment or surgery
Days 4–7
-
Root canal retreatment
or -
Apicoectomy if retreatment is not possible
-
Removal of infected tissue
Days 8–14
-
Post-treatment follow-up
-
Monitor pain and swelling
-
Evaluate healing response
Issues That Will Scale Up If Untreated
-
Expansion of apical lesion
-
Increased bone loss
-
Spread of infection to adjacent teeth
-
Facial swelling or sinus involvement
-
Tooth extraction requirement
Clinical Comments
Apical infections can remain silent for years and are often detected only on CBCT scans. Early intervention greatly improves tooth survival and prevents extensive bone damage.
Find a Dental Clinic Near You
Use our directory to locate a dental clinic near your area:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic