Strong Teeth, Fresh Breath, Brighter You.
Gum Swelling Near Back Teeth Case Analysis and Treatment Guide
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
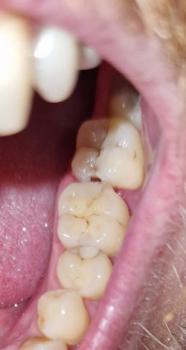
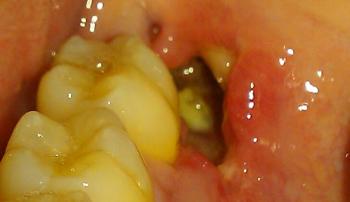
What Is Seen in This Case
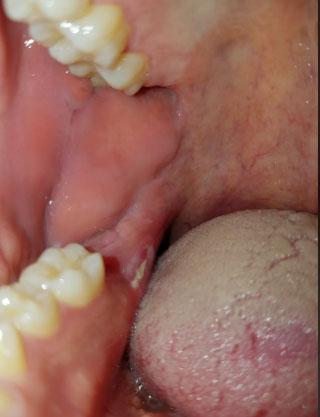
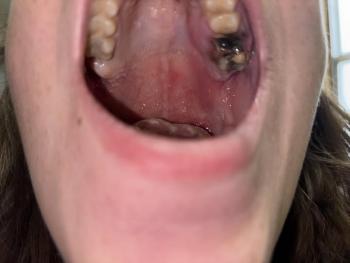
The image shows swelling and redness of the gum tissue near the back teeth, close to the lower molar area. The gum appears raised and irritated, with possible signs of underlying infection or inflammation. The nearby teeth look intact, but the soft tissue suggests a deeper problem beneath the surface.
This type of swelling often indicates gum infection related to a nearby tooth or trapped bacteria.
Most Likely Diagnosis
Based on visual examination, the most likely conditions include:
-
Localized gum infection
-
Early dental abscess near a back tooth
-
Inflammation caused by trapped food or plaque
-
Infection spreading from a nearby tooth root
A dental examination and X-ray are required to confirm the exact source.
What Causes Gum Swelling in This Area
Common causes include:
-
Untreated tooth decay nearby
-
Food debris trapped under the gum
-
Poor oral hygiene around molars
-
Gum trauma from chewing
-
Bacterial infection below the gumline
Back teeth are harder to clean, making them more prone to hidden infections.
Is This a Serious Problem
This condition can become serious if left untreated. If ignored, it may scale up into:
-
Increased pain and swelling
-
Formation of a gum or tooth abscess
-
Pus discharge
-
Facial or jaw swelling
-
Spread of infection to jawbone
-
Tooth loss
Early dental care greatly reduces these risks.
Recommended Treatment Process
Initial Assessment (Days 1–3)
-
Dental examination
-
Dental X-ray to locate infection source
-
Evaluation of nearby teeth and bone
Active Treatment Phase (Days 4–7)
Treatment may include:
-
Professional cleaning and drainage
-
Treatment of the infected tooth
-
Root canal treatment if the nerve is involved
-
Tooth extraction if the tooth cannot be saved
-
Antibiotics if infection has spread
Healing and Follow-Up (Days 8–14)
-
Swelling and redness should reduce
-
Gum tissue begins to heal
-
Pain and discomfort improve
Expected Healing Time
-
Mild gum infection: 5–7 days
-
Moderate infection or post-treatment healing: up to 14 days
Healing depends on how early treatment begins.
What Happens If Treatment Is Delayed
If delayed beyond 14 days, this condition may worsen and cause:
-
Larger abscess formation
-
Persistent pain
-
Fever and general illness
-
Bone infection
-
Emergency dental or medical care
-
Higher treatment costs
Dental infections should not be ignored.
Home Care While Waiting for Treatment
These steps help reduce discomfort but do not cure infection:
-
Rinse gently with warm salt water
-
Brush carefully around the area
-
Avoid chewing on the affected side
-
Avoid sugary foods and drinks
Seek dental care as soon as possible.
Professional Comment
This case shows localized gum swelling near back teeth, often a sign of infection below the surface. Early dental evaluation prevents infection spread, tooth damage, and serious complications.
Visit a Dental Clinic Near You
Find a nearby dental clinic using our directory:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic