Because Every Tooth Deserves Care.
Root Caries on Front Teeth | Cervical Tooth Decay Case Analysis and Treatment Guide
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
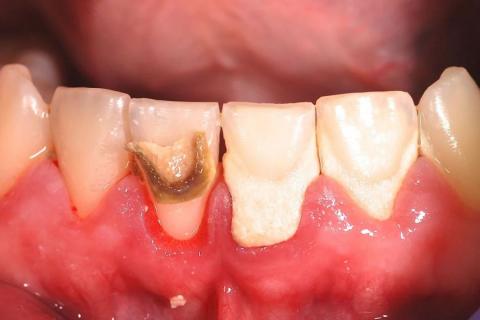
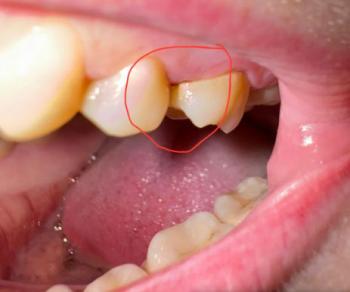
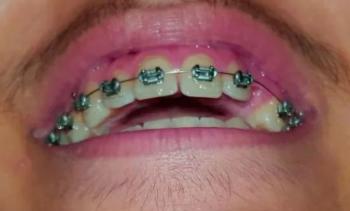
Advanced Cervical / Root Caries on Anterior Teeth – Full Case Analysis (100% Zoom)
Clinical Note: The following is an educational analysis based on the provided image. A definitive diagnosis requires an in-person dental examination, periodontal probing, and dental X-rays.
Case Overview (Zoom 100%)
The image shows localized but advanced decay at the cervical (gum-line) and root surface of an anterior tooth, with adjacent teeth also showing gingival recession. The darkened area indicates dentin/root involvement, not surface staining. The gum tissue appears inflamed and recessed, exposing softer root surfaces that are highly vulnerable to rapid decay.
Primary Diagnosis
-
Root Caries (Cervical Caries)
-
Decay has progressed into root cementum and dentin
-
Faster progression than enamel caries due to softer tooth structure
-
-
Gingival Recession
-
Gum tissue has receded, exposing the root
-
Commonly linked to periodontal disease, aggressive brushing, or occlusal stress
-
-
High Sensitivity / Early Pulp Risk
-
Lesion depth suggests proximity to the pulp
-
Risk of pulpitis if not treated promptly
-
Client-Reported Symptoms (Typical in This Case)
-
Sharp sensitivity to cold, air, or sweets
-
Occasional pain when brushing or eating
-
Gum tenderness or bleeding near the affected tooth
-
Concern about tooth appearance or dark discoloration
Deep Examination Findings (Image-Based)
-
Clearly demarcated carious lesion at the root surface
-
Loss of normal tooth contour near the gum line
-
Inflamed gingiva with reduced attachment height
-
Adjacent teeth show early risk due to recession
Can This Heal in 14 Days?
Tooth decay does NOT heal on its own.
However, 14 days is a critical window to:
-
Stop bacterial progression
-
Reduce inflammation
-
Prevent nerve infection
Without treatment, damage will continue beyond this period.
Treatment Process to Execute
Step 1: Clinical Assessment (Day 1–3)
-
Intraoral examination
-
Periapical X-ray of affected tooth
-
Periodontal evaluation
Step 2: Disease Control (Day 3–7)
-
Scaling and root planing to remove plaque and bacteria
-
Desensitizing agents if needed
-
Oral hygiene correction (brushing technique, fluoride use)
Step 3: Definitive Restoration (Day 7–14)
Depending on severity:
-
Cervical composite filling (if pulp not involved)
-
Root canal treatment (if pulp is infected)
-
Crown placement if structural integrity is compromised
-
Extraction only if the tooth is non-restorable
Expected Healing Timeline
-
Gum inflammation reduction: 7–10 days
-
Sensitivity improvement: 1–2 weeks
-
Full soft tissue stabilization: 3–4 weeks
-
Long-term stability depends on oral hygiene and recall visits
What Will Scale Up If Left Untreated
-
Rapid deepening of root decay
-
Severe tooth sensitivity and pain
-
Pulp infection and abscess formation
-
Gum and bone loss around the tooth
-
Tooth fracture or eventual tooth loss
-
Increased treatment cost and complexity
Professional Comments
-
Root caries is aggressive and time-sensitive
-
Early treatment can save the tooth and nerve
-
Delay significantly increases the risk of root canal or extraction
-
Preventive care and regular follow-ups are essential after treatment
Strong Recommendation
Please visit the nearest dental clinic as soon as possible for a full evaluation and appropriate treatment.
You may search for a clinic near your location using our dental directory:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic
Early intervention can prevent pain, infection, and tooth loss.