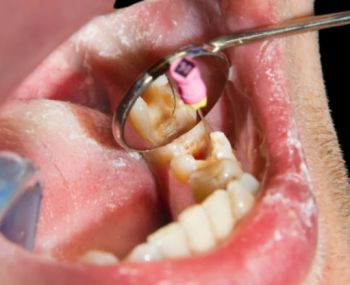
Smile Again with Comfort and Confidence.
Rare but Ruthless: How to Spot and Fight Oral Melanoma Early
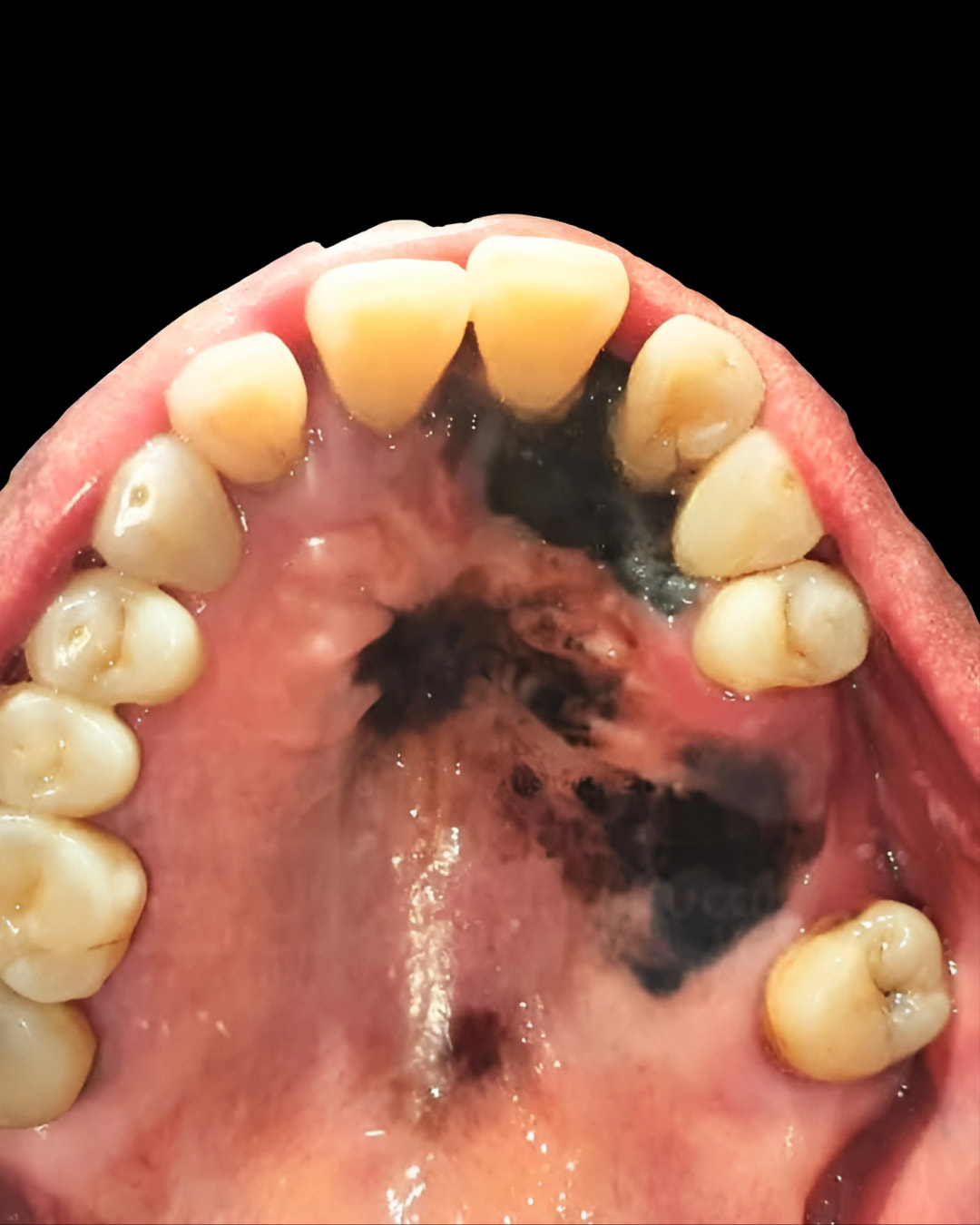
Oral Melanoma: A Rare but Deadly Oral Cancer – Expert Insights & Recovery Strategies
Oral melanoma is an aggressive and rare form of cancer that develops from melanocytes in the oral mucosa. Although it accounts for less than 8% of all melanomas, its prognosis is often poor due to late detection. Unlike skin melanomas, oral melanomas are frequently diagnosed at advanced stages, making treatment more challenging.
In this blog, we’ll explore:
✔ What oral melanoma is and where it commonly occurs
✔ Key symptoms to watch for
✔ How it’s diagnosed and treated
✔ Expert advice on improving recovery and healing
What is Oral Melanoma?
Oral melanoma arises froom pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) in the mouth. Unlike skin melanomas, which are often linked to sun exposure, the exact cause of oral melanoma remains unclear.
Common Sites in the Mouth
-
Hard palate (most frequent location)
-
Maxillary gingiva (upper gums)
-
Buccal mucosa (inner cheeks) & tongue (rare)
Warning Signs & Symptoms
Early detection is critical, but oral melanoma often grows unnoticed. Look for:
-
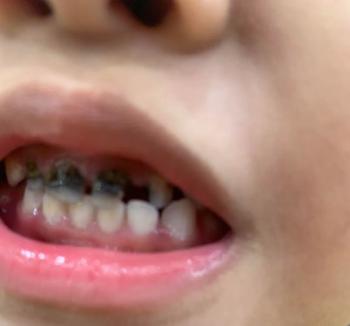
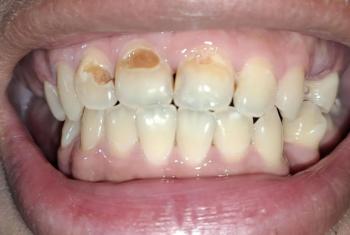
Dark patches: Brown, black, or even pink/red lesions (amelanotic melanoma).
-
Irregular borders: Asymmetric, uneven edges.
-
Rapid growthz: Sudden changes in size or color.
-
Ulceration & bleeding: In advanced stages.
Why is it often diagnosed late?
-
Painless in early stages → patients ignore it.
-
Misdiagnosed as benign pigmentation or gum disease.
How is Oral Melanoma Diagnosed?
1. Biopsy (Gold Standard)
A tissue sample is taken and examined under a microscope to confirm melanoma.
2. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
Special stains (S-100, HMB-45, Melan-A) help identify melanoma cells.
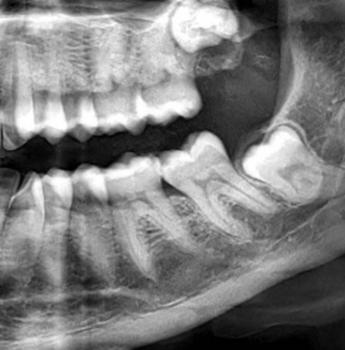
3. Imaging Tests
-
CBCT/MRI: Checks bone and soft tissue invasion.
-
PET-CT: Detects metastasis (spread to lymph nodes or other organs).
Treatment Options: Can Oral Melanoma Be Cured?
The best chance of recovery comes from early intervention. Treatment depends on the stage:
1. Surgery (Primary Treatment)
-
Wide local excision: Tumor removal with 1–2 cm margins.
-
Lymph node dissection: If cancer has spread.
2. Radiation Therapy
Used after surgery to kill remaining cancer cells or in cases where surgery isn’t possible.
3. Immunotherapy & Targeted Therapy
-
Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) & Nivolumab (Opdivo): Boost the immune system to fight cancer.
-
BRAF/MEK inhibitors (if genetic mutations are present).
4. Palliative Care (Advanced Cases)
Focuses on pain relief and improving quality of life if the cancer is incurable.
Expert Advice for Recovery & Healing
✅ 1. Early Detection Saves Lives
-
Regular dental check-ups: Dentists can spot suspicious lesions early.
-
Self-exams: Look for unusual dark spots or ulcers in your mouth.
✅ 2. Post-Treatment Care
-
Follow-up visits: Essential to monitor recurrence.
-
Oral hygiene: Prevent infections with gentle cleaning.
-
Nutrition: High-protein, vitamin-rich diet to aid healing.
✅ 3. Emotional & Psychological Support
-
Join cancer support groups.
-
Therapy can help cope with anxiety/depression.
✅ 4. Lifestyle Adjustments
-
Avoid smoking/alcohol (increases cancer risk).
-
Strengthen immunity with exercise and a balanced diet.
Prognosis: What’s the Survival Ratee?
-
Early-stage: Better outcomes if caught before spreading.
-
Advanced-stage: 5-year survival rate is <30% due to high recurrence and metastasis risk.
Final Thoughts
Oral melanoma is rare but deadly. Early diagnosis and aggressive treatment offer the best chance of survival. If you notice any unusual oral lesions, see a dentist or oral surgeon immediately.
Have questions or concerns? Consult an oral pathologist or oncologist for personalized advice.
CEBUANO TRANSLATION
Oral Melanoma: Usa ka Talagsaon Apan Delikado nga Oral nga Kanser – Mga Tambag sa Eksperto ug Estratehiya sa Pag-ayo
Ang oral melanoma usa ka agresibo ug talagsaong matang sa kanser nga nagsugod sa melanocytes sa oral mucosa. Bisan pa og ubos lang sa 8% sa tanang melanoma ang oral melanoma, kasagaran kini ma-diagnose sa ulahi nga yugto, hinungdan nga lisod ang pagtambal ug ubos ang survival rate.
Niining artikulo, atong hisgutan ang:
✔ Unsa ang oral melanoma ug asa kini kasagarang motuhaw
✔ Mga simtoma nga angay bantayan
✔ Paunsa kini ma-diagnose ug tambalan
✔ Mga tip sa recovery ug pag-ayo gikan sa mga eksperto
Unsa ang Oral Melanoma?
Ang oral melanoma gikan sa melanocytes, mga selula nga nagmugna og pigment (melanin) sulod sa baba. Dili sama sa skin melanoma nga kasagaran tungod sa adlaw, ang hinungdan sa oral melanoma wala pa gyuy klarong kasayuran.
Kasagaran nga Lokasyon sa Baba:
-
Hard palate (itib nga langitngit)
-
Maxillary gingiva (itaas nga mga lagos/gums)
-
Buccal mucosa (sulod sa aping) ug dila (talagsaon)
Mga Ilhanan ug Simtoma:
-
Itom, brown, o pula nga patch o lesion
-
Walay regular nga gilid (irregular borders)
-
Kalit nga pagtubo o kausaban sa kolor/size
-
Ulser ug pagdugo sa ulahi nga yugto
Ngano nga ulahi kasagaran ang diagnosis?
✔ Wala’y kasakit sa sugod → pasyente magpasagad
✔ Makasayop og diagnose isip "pigment" lang o gingivitis
Giunsa Pag-Diagnose ang Oral Melanoma?
-
Biopsy (Gold Standard) – Paghugot og sample sa tisyu para maeksamin sa microscope
-
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) – Gamit og specific stains (S-100, HMB-45, Melan-A)
-
Imaging Tests
-
CBCT/MRI – Tan-awon kung ang bukog o soft tissue naigo
-
PET-CT – Para sa metastasis (pagkatay sa laing parte sa lawas)
-
Mga Tambal: Maayo Pa Ba ang Oral Melanoma?
Ang pinakamaayong chance sa pagkaayo mao ang early detection ug intervention. Depende sa stage ang tambal:
-
Surgery – Pagkuha sa tumor gamit ang 1–2 cm nga gilay-on (margin)
-
Radiation Therapy – Para patyon ang nahabilin nga cancer cells
-
Immunotherapy / Targeted Therapy
-
Pembrolizumab / Nivolumab – Palig-on sa immune system
-
BRAF/MEK inhibitors – Kung naay specific genetic mutation
-
-
Palliative Care – Para sa kasakit ug kalidad sa kinabuhi sa dili na matambalan
Tambag sa Eksperto para sa Recovery:
✅ 1. Sayong Detection Makatabang sa Kinabuhi
-
Regular dental check-ups
-
Self-exam sa baba
✅ 2. Pag-atiman Human sa Tambal
-
Follow-up visits
-
Maayo nga oral hygiene
-
Nutrisyon nga puno og protina ug bitamina
✅ 3. Suporta sa Emosyonal ug Mental nga Aspeto
-
Apil sa support group
-
Therapy batok sa kabalaka o depresyon
✅ 4. Healthy Lifestyle
-
Likayi ang panigarilyo ug alkohol
-
Lig-ona ang resistensya pinaagi sa diet ug ehersisyo
Prognosis: Survival Rate
-
Early-stage: Mas taas ang chance mabuhi
-
Advanced-stage: Mas ubos, 5-year survival rate ubos pa sa 30%
Huna-huna sa Katapusan:
Bisan talagsaon, delikado kaayo ang oral melanoma. Sayong pagdiagnose ug agresibong tambal ang pinaka-epektibo nga depensa. Kung naa kay makita nga dili kasagaran nga itom nga patik, bisitaha dayon ang dentista o oral surgeon.
TAGALOG TRANSLATION
Oral Melanoma: Isang Bihira Pero Nakakamatay na Uri ng Oral Cancer – Mga Ekspertong Payong Medikal at Estratehiya sa Paggaling
Ang oral melanoma ay isang bihira pero agresibong uri ng cancer na nagsisimula sa melanocytes (pigment cells) sa loob ng bibig. Bagamat bumubuo lamang ito ng mas mababa sa 8% ng lahat ng kaso ng melanoma, mababa ang survival rate dahil karaniwang huli na itong nade-detect.
Sa blog na ito, tatalakayin natin ang:
✔ Ano ang oral melanoma at saan ito kadalasang lumalabas
✔ Mga pangunahing sintomas na dapat bantayan
✔ Paano ito nade-diagnose at ginagamot
✔ Mga payo ng eksperto para sa paggaling
Ano ang Oral Melanoma?
Ito ay nagmumula sa mga melanocytes sa loob ng bibig. Di tulad ng skin melanoma na kaugnay ng araw, hindi pa tiyak ang sanhi ng oral melanoma.
Karaniwang Lugar na Apektado:
-
Hard palate (matigas na bahagi ng ngalangala)
-
Maxillary gingiva (itaas na gilagid)
-
Buccal mucosa (loob ng pisngi) at dila (bihira)
Mga Sintomas at Babala:
-
Maitim, kayumanggi, o mapulang mga patch o sugat
-
Hindi pantay ang gilid o hugis
-
Mabilis lumaki o magbago ng kulay
-
Pagkakaroon ng sugat at pagdurugo sa mas malalang yugto
Bakit kadalasang huli ang diagnosis?
✔ Walang sakit sa simula kaya hindi pinapansin
✔ Napagkakamalang simpleng pigmentation o gingivitis
Paano Na-Di-Diagnose ang Oral Melanoma?
-
Biopsy (Gold Standard) – Kumuha ng sample tissue at suriin sa microscope
-
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) – Paggamit ng specific stain (S-100, HMB-45, Melan-A)
-
Imaging
-
CBCT/MRI – Para tingnan kung apektado ang buto o tissue
-
PET-CT – Para malaman kung kumalat sa ibang parte ng katawan
-
Mga Gamot at Lunas: Pwede Pa Bang Gumaling?
Oo—lalo na kung maaga ang pagkakatuklas. Depende sa stage ng cancer:
-
Surgery – Pagputol sa tumor na may 1–2 cm margin
-
Radiation Therapy – Para patayin ang natitirang cancer cells
-
Immunotherapy / Targeted Therapy
-
Pembrolizumab / Nivolumab – Pampalakas ng immune system
-
BRAF/MEK inhibitors – Kung may genetic mutation
-
-
Palliative Care – Para sa sakit at kalidad ng buhay kung hindi na magagamot
Payo ng Eksperto sa Paggaling:
✅ 1. Maagang Pagkilala sa Sintomas ay Nagliligtas ng Buhay
-
Regular na dental check-up
-
Self-check sa loob ng bibig
✅ 2. Pag-aalaga Matapos ang Gamutan
-
Follow-up checkups
-
Malinis na kalinisan sa bibig
-
Nutrisyong mayaman sa protina at bitamina
✅ 3. Suportang Emosyonal at Mental
-
Sumali sa cancer support groups
-
Therapy laban sa anxiety o depresyon
✅ 4. Bagong Lifestyle
-
Iwasan ang sigarilyo at alak
-
Palakasin ang katawan sa pamamagitan ng tamang pagkain at ehersisyo
Prognosis: Survival Rate
-
Early stage: Mas mataas ang tsansa ng paggaling
-
Late stage: Mababa—mas mababa sa 30% ang 5-year survival rate
Panghuling Paalala:
Ang oral melanoma ay bihira pero mapanganib. Ang maagang pagtuklas at agresibong paggamot ang susi sa kaligtasan. Kung may kakaibang patik, itim na bahagi, o sugat sa bibig—kumonsulta agad sa dentista o oral surgeon.