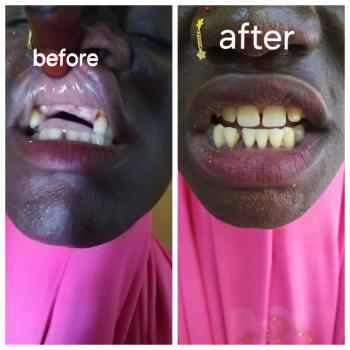
We Bring Back the Sparkle in Your Smile.
Root Canal Infection With Apical Bone Loss - Dental Case Analysis
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
Dental Case Analysis – Root Canal Infection With Apical Bone Loss
Case Overview
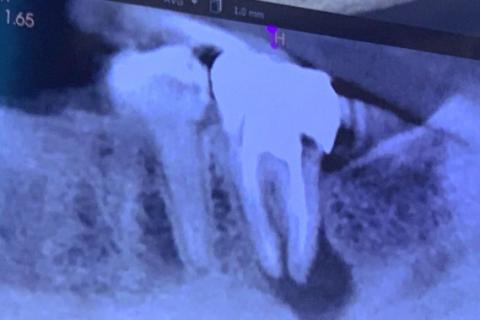
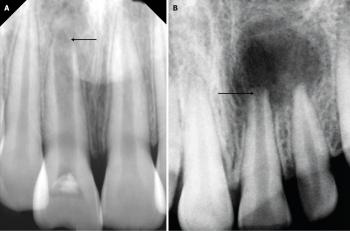
This dental X-ray shows a posterior tooth with previous root canal treatment. A clear radiolucent area at the root apex is visible, indicating a persistent or recurrent infection. The surrounding bone shows signs of loss consistent with chronic inflammation.
Full Analysis and Diagnosis
Radiographic Findings
-
Root canal–treated tooth with dense coronal restoration
-
Apical radiolucency at the root tip
-
Loss of normal bone trabeculation
-
Widened periodontal ligament space
-
Infection appears chronic rather than acute
Tooth Condition
-
Root canal filling may be incomplete or leaking
-
Possible missed canal or bacterial persistence
-
Apical seal likely compromised
-
Tooth structure remains intact but weakened
Diagnosis
-
Chronic apical periodontitis
-
Failed or compromised root canal treatment
-
Localized periapical bone loss
Time Frame to Heal
With Proper Treatment
-
Infection control: 7–14 days
-
Reduction in inflammation: 1–2 weeks
-
Bone healing begins: 4–6 weeks
-
Radiographic bone regeneration: 3–6 months
Without Treatment
-
Infection persists or enlarges
-
Progressive bone destruction
-
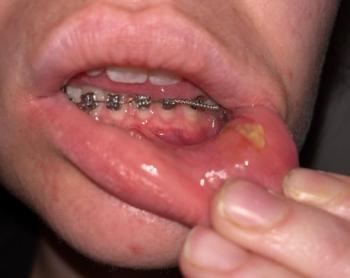
Pain, swelling, or abscess formation
-
Increased risk of tooth loss
Process to Execute (14-Day Window)
Days 1–3
-
Clinical evaluation and X-ray review
-
Confirm infection source
-
Prescribe antibiotics if clinically indicated
Days 4–7
-
Root canal retreatment or
-
Surgical intervention (apicoectomy) if retreatment is not possible
-
Removal of infected tissue
Days 8–14
-
Post-treatment evaluation
-
Monitor symptoms and healing
-
Plan long-term restoration if needed
Issues That Will Scale Up If Untreated
-
Expansion of apical lesion
-
Further jawbone loss
-
Chronic pain or swelling
-
Sinus or nerve involvement (depending on location)
-
Eventual tooth extraction
Clinical Comments
This type of infection can remain silent for long periods and is often discovered only through imaging. Early intervention significantly improves the chance of saving the tooth and preventing further bone loss.
Find a Dental Clinic Near You
Search for a qualified dental clinic in your area:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic