Your Smile, Our Passion.
Infected Back Tooth With Gum Swelling Case Analysis
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
What Is Seen in This Case
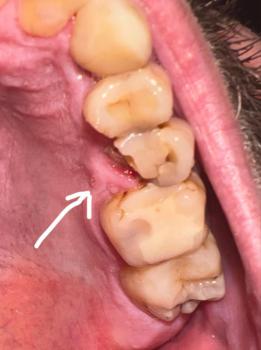
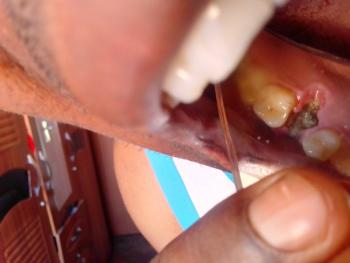
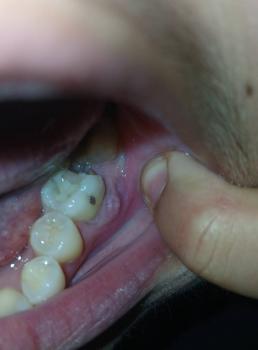
The image shows a back tooth with visible decay and a red swollen gum area beside it. There appears to be a dark cavity on the tooth surface, with surrounding gum tissue inflamed and irritated. This pattern often indicates tooth decay with early infection affecting the gum.
The swelling suggests bacteria have progressed beyond the tooth surface.
Most Likely Diagnosis
Based on visual assessment, the most likely conditions include:
-
Dental caries on a back tooth
-
Localized gum infection near the decayed tooth
-
Early dental abscess formation
-
Plaque and food debris trapped near the tooth
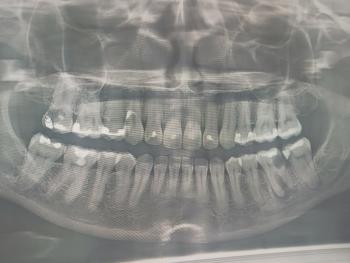
A dental examination and X-ray are required to confirm the depth of infection.
What Causes This Condition
Common causes include:
-
Untreated cavities
-
Delayed dental visits
-
Food trapped between back teeth
-
Poor oral hygiene around molars
-
Broken or weakened tooth structure
When decay reaches deeper layers, bacteria irritate the surrounding gum tissue.
Is This a Serious Problem
This condition is moderate to serious. If left untreated, it may scale up into:
-
Severe toothache
-
Gum abscess with pus
-
Facial swelling
-
Spread of infection to nearby teeth
-
Tooth loss
-
Jawbone infection in advanced cases
Early treatment greatly reduces complications.
Recommended Treatment Process
Initial Assessment (Days 1–3)
-
Dental examination
-
Dental X-ray to assess decay depth
-
Evaluation of gum swelling and infection
Active Treatment Phase (Days 4–7)
Treatment depends on severity and may include:
-
Removal of decayed tooth structure
-
Dental filling or crown
-
Root canal treatment if nerve is infected
-
Antibiotics if active infection is present
-
Tooth extraction if the tooth cannot be saved
Healing and Follow-Up (Days 8–14)
-
Swelling should gradually reduce
-
Gum tissue begins to heal
-
Pain and discomfort improve
Expected Healing Time
-
Mild gum infection: 7–10 days
-
Post-treatment healing: up to 14 days
Healing speed depends on how early treatment is started.
What Happens If Treatment Is Delayed
If ignored for more than 14 days, this condition may lead to:
-
Abscess enlargement
-
Severe pain
-
Fever
-
Facial or jaw swelling
-
Higher treatment cost
-
Increased risk of tooth loss
Dental infections should not be delayed.
Home Care While Waiting for Treatment
These steps help reduce irritation but do not cure infection:
-
Rinse with warm salt water
-
Brush gently twice daily
-
Avoid chewing on the affected side
-
Avoid sugary foods and drinks
Seek dental care as soon as possible.
Professional Comment
This case shows active tooth decay with gum involvement, a clear warning sign of infection. Early dental treatment protects the tooth, controls infection, and prevents serious complications.
Visit a Dental Clinic Near You
Find a nearby dental clinic using our directory:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic