Dentures That Feel Natural, Look Beautiful.
Severe Tooth Decay With Gum Infection | Dental Abscess Case Analysis and Treatment Guide
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
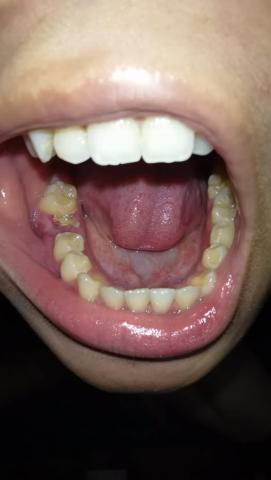
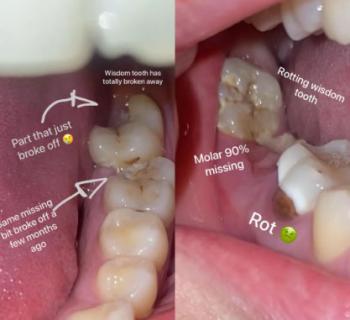
Advanced Molar Tooth Decay With Gum Infection – Full Dental Case Analysis (100% Zoom)
Medical Disclaimer
This assessment is image-based and educational. A final diagnosis requires an in-person dental examination, X-rays, and vitality testing. However, visible signs strongly indicate a serious and urgent dental condition that needs immediate professional care.
Case Overview (Zoom 100%)
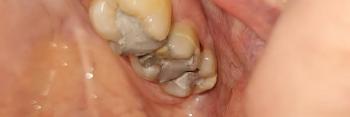
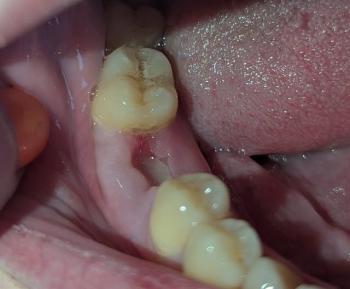
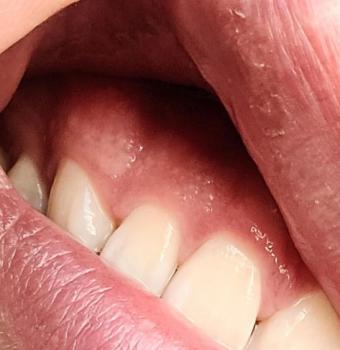
The image clearly shows a severely decayed lower molar with a large open cavity, food impaction, and inflamed surrounding gum tissue. The gum near the affected tooth appears swollen and irritated, suggesting active bacterial infection. Adjacent teeth are at risk due to plaque retention and bacterial spread.
This is not an early cavity—the decay has likely reached deep dentin and possibly the pulp (nerve).
Primary Diagnosis
-
Severe Dental Caries (Advanced Tooth Decay)
-
Large cavitated lesion
-
Structural tooth breakdown
-
High likelihood of nerve involvement
-
-
Localized Gingival Infection / Early Dental Abscess
-
Gum swelling near the decayed tooth
-
Possible pus formation beneath the surface
-
Pain and pressure likely present
-
-
High Risk of Pulpitis or Necrotic Pulp
-
Bacteria likely approaching or invading the pulp chamber
-
Client-Reported Symptoms (Common in This Case)
-
Persistent toothache or throbbing pain
-
Pain when chewing
-
Sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods
-
Swollen or sore gums
-
Bad taste or foul odor in the mouth
Deep Clinical Examination (Image-Based)
-
Extensive enamel and dentin loss
-
Plaque and food debris trapped inside the cavity
-
Inflamed soft tissue surrounding the tooth
-
Adjacent teeth vulnerable to secondary decay
Can This Heal in 14 Days?
No — advanced tooth decay does not heal naturally.
However, 14 days is a critical intervention period to:
-
Stop infection progression
-
Relieve pain
-
Prevent abscess spread or jawbone involvement
Delaying treatment beyond this period greatly increases complications.
What Will Scale Up If Left Untreated
Within 1–2 Weeks
-
Severe, constant pain
-
Increased gum swelling
-
Possible pus discharge
Within 1 Month
-
Dental abscess formation
-
Jawbone infection
-
Facial swelling
Long-Term
-
Tooth loss
-
Spread of infection to surrounding teeth
-
Risk of systemic infection (dangerous if untreated)
Recommended Treatment Process
Step 1: Urgent Dental Assessment (Day 1–2)
-
Clinical examination
-
Dental X-ray to assess nerve and bone
-
Pain and infection control
Step 2: Infection Control (Day 2–5)
-
Temporary medication if needed
-
Drainage if abscess is present
-
Oral hygiene guidance
Step 3: Definitive Treatment (Day 5–14)
Depending on tooth condition:
-
Root canal treatment (if tooth is restorable)
-
Crown placement after infection control
-
Tooth extraction if damage is extensive
Expected Healing Timeline
-
Pain relief: 1–3 days after treatment starts
-
Gum swelling reduction: 5–10 days
-
Soft tissue healing: 2–3 weeks
-
Full recovery depends on procedure performed
Professional Comments
-
This is a high-risk and urgent dental emergency
-
Pain may temporarily stop but infection continues silently
-
Home remedies will not eliminate bacteria
-
Early treatment can still save the tooth and prevent surgery
Strong Recommendation
Please visit the nearest dental clinic immediately for proper diagnosis and treatment.
You may find a dental clinic near your area using our directory listing:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic
Prompt care can prevent serious infection and permanent tooth loss.