Your Smile, Perfected with Precision.
Gum Recession and Infection Above Upper Front Teeth
Severity:
Gum Recession and Infection Above Upper Front Teeth Case Analysis
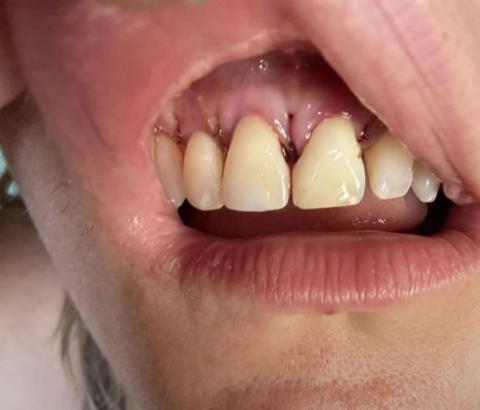
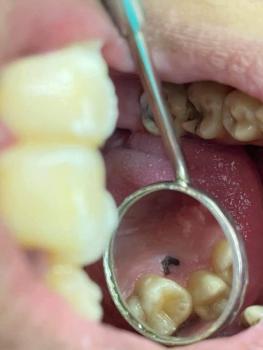
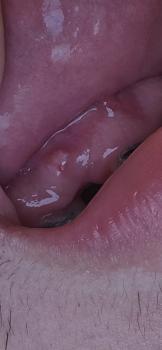
What Is Seen in This Case
The image shows receded and inflamed gum tissue above the upper front teeth. The gums appear pulled upward, exposing more of the tooth surface near the gumline. There are also signs of redness and irritation, indicating inflammation and possible early infection.
This condition affects the esthetic (smile) zone, making it noticeable and concerning for patients.
Most Likely Diagnosis
Based on visual examination, the most likely conditions include:
-
Gum recession with localized inflammation
-
Early periodontal (gum) infection
-
Gum irritation caused by plaque buildup
-
Possible trauma from brushing or biting
-
Early gum abscess formation in the upper front area
A dental exam and X-ray can confirm whether bone loss or deeper infection is present.
What Causes Gum Recession and Infection in Front Teeth
Common causes include:
-
Aggressive tooth brushing
-
Plaque and tartar buildup along the gumline
-
Untreated gum disease
-
Teeth grinding or clenching
-
Thin or sensitive gum tissue
Front teeth are especially vulnerable because the gum tissue is naturally thinner.
Is This a Serious Problem
This condition may start as mild to moderate, but if untreated it can scale up into:
-
Worsening gum recession
-
Tooth sensitivity
-
Gum abscess development
-
Bone loss around the teeth
-
Tooth loosening
-
Cosmetic changes to the smile
Early care is important to stop progression.
Recommended Treatment Process
Initial Assessment (Days 1–3)
-
Dental examination
-
Gum depth and recession assessment
-
Dental X-ray if bone involvement is suspected
Active Treatment Phase (Days 4–7)
Treatment may include:
-
Professional dental cleaning
-
Removal of plaque and tartar
-
Treatment of gum infection
-
Desensitizing or protective therapy if needed
Healing and Follow-Up Phase (Days 8–14)
-
Gum inflammation should reduce
-
Tissue irritation improves
-
Gum condition stabilizes
Advanced cases may need periodontal treatment.
Expected Healing Time
-
Mild inflammation: 3–5 days
-
Moderate gum infection: 7–14 days
-
Receded gums do not regrow but can be stabilized
What Happens If Treatment Is Delayed
Delaying care may result in:
-
Continued gum recession
-
Increased tooth sensitivity
-
Bone loss around front teeth
-
Higher risk of tooth loss
-
More complex and costly treatment
Home Care While Waiting for Treatment
These steps may help reduce irritation:
-
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush
-
Brush gently along the gumline
-
Floss carefully once daily
-
Rinse with warm salt water
-
Avoid smoking and acidic foods
Seek dental care if pain or swelling increases.
Professional Comment
This case shows gum recession with signs of inflammation above the upper front teeth. Early dental intervention can stabilize the gums, reduce infection risk, and protect the appearance of the smile.
Visit a Dental Clinic Near You
For gum evaluation and periodontal care, visit:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic