Because Every Tooth Deserves Care.
Gum Recession on Lower Front Teeth | Causes, Treatment, and Prevention
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
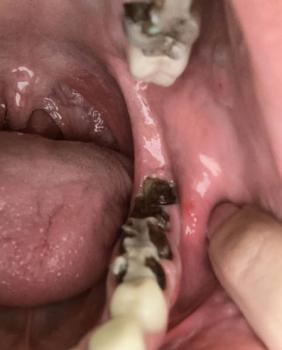
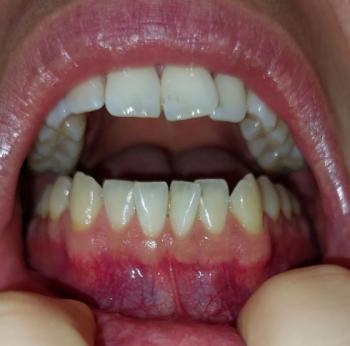
Gum Recession and Cervical Tooth Wear on Lower Front Teeth – Full Dental Case Analysis (100% Zoom)
Medical Disclaimer
This analysis is image-based and for educational purposes only. A definitive diagnosis requires an in-person dental examination, periodontal probing, and dental X-rays. The findings below are based on visible clinical signs and standard dental guidelines.
Case Overview (Zoom 100%)
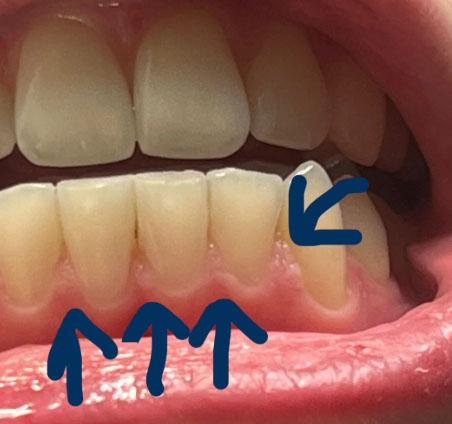
The image shows the lower anterior teeth with visible gum recession, particularly in the area indicated by arrows. The gum margin has migrated downward, exposing the cervical (neck) portion of the teeth. The tooth surfaces appear smooth and light in color, suggesting non-carious cervical lesions rather than active decay.
The arrows likely point to:
-
Exposed root surfaces
-
Thinning gum tissue
-
Loss of normal gum scalloping
This condition is progressive but manageable if treated early.
Primary Diagnosis
-
Gingival recession (localized, lower anterior region)
-
Exposed root surfaces (cementum/dentin exposure)
-
Non-carious cervical lesions (abrasion or erosion)
-
Increased risk of root sensitivity and future root caries
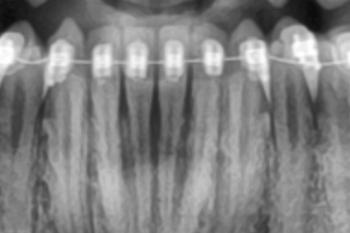
Deep Clinical Examination (Image-Based Findings)
-
Gum margin positioned apical to normal level
-
Pale pink but thin gingival tissue
-
No obvious pus or acute infection
-
Tooth color difference between enamel and exposed root
-
Likely contributing factors:
-
Aggressive brushing
-
Thin gum biotype
-
Plaque-induced inflammation
-
Occlusal stress or crowding
-
Can This Heal in 14 Days?
Gum recession does not grow back naturally.
However, within 14 days, professional care can:
-
Stop further recession
-
Reduce inflammation
-
Decrease sensitivity
-
Protect exposed root surfaces
Early intervention is critical to prevent progression.
Recommended Treatment Process
Step 1: Periodontal Evaluation (Days 1–3)
-
Periodontal probing
-
Assessment of gum thickness (biotype)
-
Evaluation of brushing technique and bite forces
Step 2: Disease Control (Days 3–7)
-
Professional scaling and polishing
-
Removal of plaque at the gum line
-
Instruction on proper brushing technique
-
Desensitizing agents if sensitivity is present
Step 3: Protective and Corrective Treatment (Days 7–14)
Depending on severity:
-
Fluoride or desensitizing varnish
-
Cervical composite fillings (if root wear is significant)
-
Occlusal adjustment if traumatic bite is present
-
Periodontal referral if recession progresses
Expected Healing Timeline
-
Inflammation reduction: 7–10 days
-
Sensitivity improvement: 1–2 weeks
-
Long-term stability: depends on oral hygiene and habit correction
Gum tissue will stabilize but will not regenerate without surgery.
What Will Escalate If Untreated
-
Increased tooth sensitivity
-
Higher risk of root caries
-
Further gum recession
-
Aesthetic concerns (longer-looking teeth)
-
Possible tooth mobility in advanced cases
Professional Comments
This is a common and manageable condition. Many patients notice recession only after sensitivity or visual changes appear. Early professional care can halt progression and protect the teeth for decades.
The condition is not an emergency, but it should not be ignored.
Strong Recommendation
Schedule a dental visit for periodontal evaluation and preventive care.
You may locate a dental clinic near your area using this directory:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic
Early intervention prevents costly and invasive procedures later.