Your Smile, Perfected with Precision.
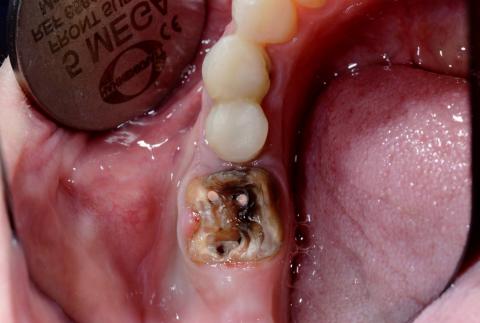
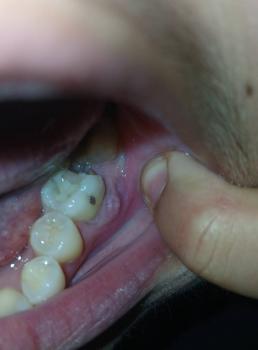
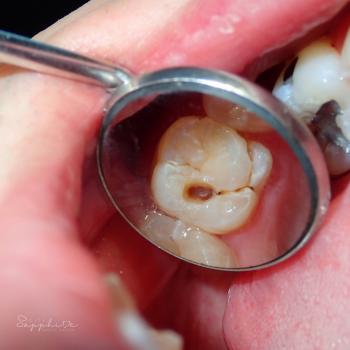
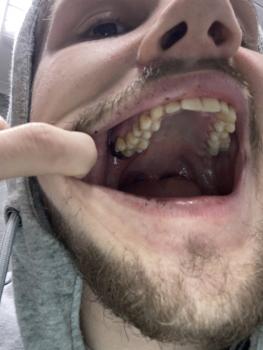
Severe Open Carious Molar With Pulp Exposure Causing Pain, Infection, and Oral Odor
Severity:
Visual Examination (Zoom 100% – Clinical Findings)
Tooth involved:
-
Lower posterior molar (likely first or second molar)
Observed conditions:
-
Extensive crown destruction due to advanced dental caries
-
Open pulp chamber clearly visible
-
Dark brown to black necrotic dentin
-
Two exposed root canal orifices
-
Food debris and bacterial biofilm present
-
Surrounding gingiva appears inflamed
-
Strong likelihood of active bacterial infection
Odor source:
-
Caused by anaerobic bacteria breaking down necrotic pulp tissue
-
Produces sulfur compounds → foul smell
Primary Diagnosis
Advanced Dental Caries With Pulp Necrosis
Complicated by:
-
Symptomatic irreversible pulpitis → progressing to pulp necrosis
-
Possible acute apical periodontitis
-
High risk of periapical abscess formation
Why the Tooth Is Painful and Smelly
| Symptom | Cause |
|---|---|
| Pain | Exposed nerve tissue + bacterial toxins |
| Smell | Dead pulp tissue + anaerobic bacteria |
| Sensitivity | Loss of enamel & dentin protection |
| Throbbing | Inflammatory pressure inside root canals |
Time Frame to Heal (If Treated Properly)
With Immediate Treatment
-
Pain relief: 24–72 hours
-
Infection control: 5–7 days
-
Root canal completion: 7–14 days
-
Final crown placement: 2–4 weeks
If Delayed or Ignored
-
Infection may spread within 7–14 days
-
Bone loss around tooth root
-
Facial swelling or jaw infection
-
Tooth may become non-restorable
Recommended Treatment Process
Step 1: Emergency Assessment
-
Digital X-ray (periapical)
-
Vitality testing
-
Infection extent evaluation
Step 2: Infection Control
-
Start antibiotics only if swelling/systemic symptoms present
-
Pain management
Step 3: Definitive Treatment (Choose One)
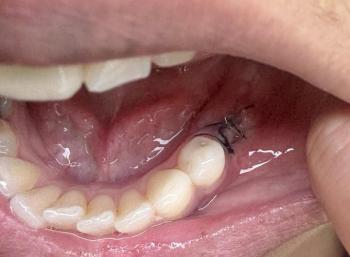
Option A: Root Canal Treatment (Preferred if tooth is restorable)
-
Complete canal debridement
-
Disinfection
-
Root filling
-
Post & crown restoration
Option B: Tooth Extraction
-
Required if:
-
Roots are fractured
-
Severe bone loss
-
Infection is uncontrollable
-
-
Followed by:
-
Dental implant
-
Bridge
-
Partial denture
-
What Will Scale Up If Untreated
-
Dental abscess
-
Jawbone infection (osteomyelitis)
-
Facial cellulitis
-
Sinus involvement (upper teeth)
-
Bad breath becomes chronic
-
Tooth loss
-
Risk of systemic infection (rare but serious)
Clinical Comments
This tooth is beyond simple filling repair. The pulp is already compromised. Home remedies, mouthwash, or antibiotics alone will not cure this condition. Definitive dental intervention is required immediately.
Visit a Nearby Dental Clinic (Cebu Area)
To find a licensed dental clinic near you, use our verified directory:
Search Dental Clinics Here:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic