Your Smile, Our Passion.
Gum Recession from Bruxism and Hard Brushing: Causes, Fixes, and Healing Timeline
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
Case Analysis: Gum Recession and Enamel Wear – Traumatic Occlusion & Bruxism
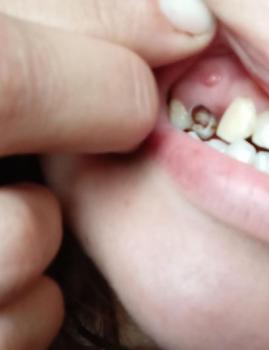
Client’s Complaint
“I’ve noticed my gums pulling away from my teeth and some yellowish parts near the roots. One dentist said it’s from grinding or clenching, another said from brushing too hard. What’s really happening?”
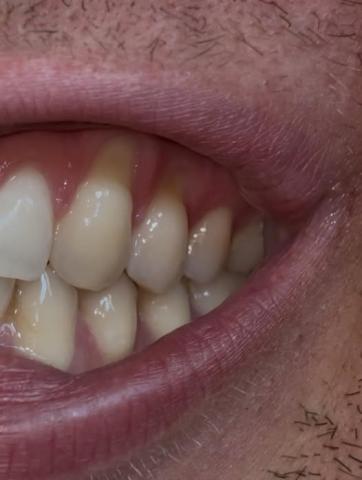
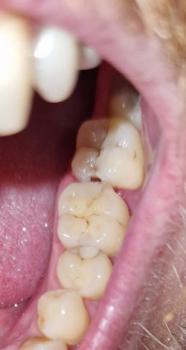
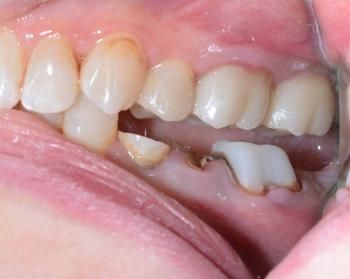
Clinical Observation (from Image)
After zooming in:
-
Noticeable gum recession (gingival margin has pulled away) around the upper premolars.
-
Exposed root surfaces appear slightly yellow compared to enamel — typical for dentin exposure.
-
No major inflammation, meaning the cause is likely mechanical, not bacterial.
-
Teeth alignment shows mild forward tilt and contact stress marks — consistent with traumatic occlusion.
Probable Diagnosis
1. Gingival Recession due to Traumatic Occlusion
-
Repeated biting stress and grinding create micro-trauma on the gums and bone.
-
The gum recedes slowly, exposing the root surface.
2. Bruxism (Clenching/Grinding Habit)
-
Common during sleep or stress.
-
Causes enamel wear, gum recession, and root sensitivity.
3. Toothbrush Abrasion (Contributing Factor)
-
Hard brushing with stiff bristles or horizontal scrubbing damages gum tissue.
-
This worsens the gum loss caused by bruxism.
Why This Happened (Short Story)
The client’s teeth have been under constant pressure — both from grinding during sleep and overbrushing while trying to keep them clean.
Over time, the gums began to retreat, exposing the darker root area.
What used to be a strong brushing habit turned into an abrasive routine that, paired with jaw tension, led to visible gum wear.
This is a classic example of how mechanical habits — even good intentions like brushing — can harm your smile if done too harshly or without awareness of grinding.
Treatment & Management Plan
1. Protect Teeth from Grinding
-
Night Guard (Occlusal Splint): Custom-made device to prevent tooth wear and cushion pressure.
-
Stress Management: Grinding is often linked to anxiety and tension.
2. Correct Brushing Technique
-
Use soft-bristled toothbrush only.
-
Gentle circular motions, not side-to-side scrubbing.
-
Consider electric toothbrush with pressure sensor.
3. Treat Gum Recession
-
Desensitizing toothpaste (for exposed roots).
-
Fluoride varnish to protect exposed dentin.
-
Gum grafting (if recession is severe) to restore coverage.
4. Adjust Bite (If Needed)
-
Dentist may perform bite equilibration or orthodontic adjustment to relieve stress on key teeth.
Healing and Maintenance
-
Minor inflammation improves within 1–2 weeks after reducing trauma.
-
Gum reattachment or graft healing: 4–8 weeks.
-
Bruxism control is long-term — ongoing monitoring and night guard use are crucial.
Comment (for blog or clinic use)
Gum recession isn’t always caused by poor hygiene — often, it’s due to habits like grinding, clenching, or brushing too hard. Protecting your gums means being gentle and aware of daily pressure on your teeth. If you notice receding gums or root exposure, visit your trusted dental specialist today through CebuDentalImplants.com to prevent further damage and restore a healthy smile.