Strong Teeth, Fresh Breath, Brighter You.
Severely Carious Primary Anterior Teeth: Full Clinical Analysis, Diagnosis, and Best Material for Rebuilding
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
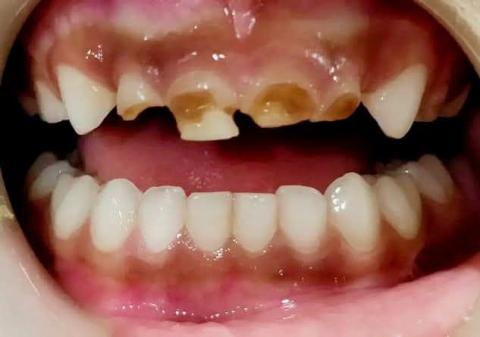
Zoom 100% – Visual Examination (Primary Dentition)
Observed Findings:
-
Severe early childhood caries (ECC) affecting maxillary primary incisors
-
Extensive enamel loss with exposed dentin
-
Brownish cavitated lesions indicating advanced dentinal caries
-
Structural collapse of incisal edges
-
Gingival tissues appear mildly inflamed but without obvious abscess at this stage
-
Mandibular incisors appear intact and healthy
Full Diagnosis
Primary Diagnosis:
-
Severe Early Childhood Caries (S-ECC)
-
Gross crown destruction of maxillary primary incisors
Contributing Factors:
-
Prolonged bottle feeding or frequent sugary drinks
-
Poor oral hygiene in early childhood
-
Weak enamel mineralization
-
Delayed dental intervention
Client Question Answered
“What material is most suitable for rebuilding these badly damaged primary teeth?”
✅ BEST MATERIAL OPTIONS (RANKED)
1. Prefabricated Zirconia Crowns (BEST OPTION)
Why it’s ideal:
-
Extremely durable for primary teeth
-
Excellent aesthetics (natural tooth color)
-
Resistant to recurrent caries
-
Smooth surface reduces plaque accumulation
Indication:
-
Teeth with extensive structural loss
-
Cooperative child or treatment under sedation/GA
2. Resin Composite Strip Crowns
Advantages:
-
Highly aesthetic
-
Tooth-colored
-
Minimally invasive
Limitations:
-
Less durable than zirconia
-
Technique-sensitive
-
May fracture in heavy bite cases
Best for:
-
Moderate crown loss with remaining tooth structure
3. Glass Ionomer Cement (GIC) – TEMPORARY
Advantages:
-
Fluoride release
-
Chemical bonding to tooth
-
Moisture tolerant
Limitations:
-
Weak strength
-
Poor aesthetics
-
Not suitable for long-term anterior restorations
Use only as:
-
Interim restoration
-
Emergency stabilization
Not Recommended
-
Stainless steel crowns (poor esthetics for anterior teeth)
-
Amalgam (obsolete for primary anterior teeth)
Treatment Process to Execute
Step-by-Step Clinical Plan
Day 1
-
Full clinical exam + radiographs (if possible)
-
Caries excavation
-
Pulp vitality assessment
If pulp is involved:
-
Perform pulpotomy or pulpectomy
Restorative Phase
-
Tooth preparation
-
Placement of:
-
Zirconia crown OR
-
Composite strip crown
-
Fluoride varnish application
Time Frame to Heal
| Phase | Expected Time |
|---|---|
| Soft tissue healing | 7–10 days |
| Full adaptation & comfort | 10–14 days |
| Crown longevity | Until natural exfoliation |
Yes, 14 days is sufficient for complete tissue adaptation if no infection is present.
If Left Untreated – Issues That Will Scale Up
-
Dental abscess formation
-
Facial swelling
-
Pain and feeding difficulty
-
Speech development problems
-
Damage to underlying permanent tooth buds
-
Premature tooth loss → malocclusion
Professional Comments
-
Early intervention prevents orthodontic and speech complications
-
Parent education is critical to prevent recurrence
-
Regular fluoride application and dietary counseling required
-
Zirconia crowns offer the best long-term success rate
Find a Nearby Dental Clinic
Visit your nearest pediatric or family dental clinic using our directory:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic