Because Every Tooth Deserves Care.
Swollen Gums Around Lower Front Teeth in Child
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
Swollen Gums Around Lower Front Teeth in Child Case Analysis
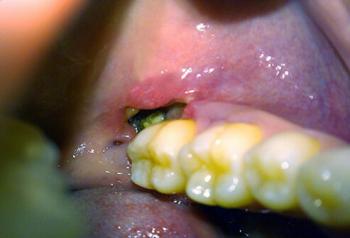
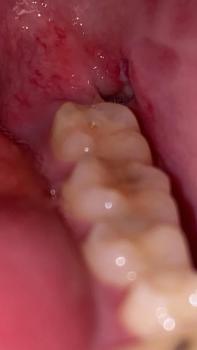
What Is Seen in This Case
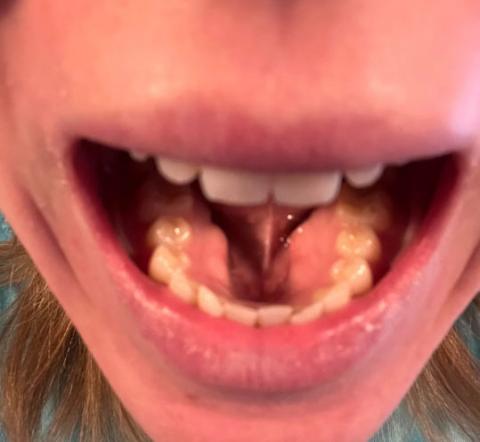
The image shows swollen, raised gum tissue around the lower front teeth, with both sides appearing bulky and inflamed. The swelling is symmetrical near the lower canine–incisor area. The teeth themselves look present, but the gum tissue is enlarged and irritated.
This pattern is commonly seen in children or young patients, especially during tooth eruption or early gum inflammation.
Most Likely Diagnosis
Based on visual examination, the most likely conditions include:
-
Eruption-related gum swelling
-
Gingival inflammation (early gingivitis)
-
Plaque-related gum irritation
-
Localized gum infection without pus
-
Normal tissue response during tooth development
A dental exam helps rule out abscess or deeper infection.
What Causes Swollen Gums in Lower Front Teeth
Common causes include:
-
Erupting permanent teeth pushing through the gums
-
Plaque buildup due to incomplete brushing
-
Food debris trapped near the gumline
-
Hormonal or growth-related gum sensitivity
-
Minor gum trauma
Children often experience gum swelling during mixed dentition stages.
Is This a Serious Problem
In most cases, this condition is mild and temporary. However, if untreated or ignored, it may scale up into:
-
Persistent gum inflammation
-
Pain or bleeding during brushing
-
Development of gum infection
-
Bad breath
-
Increased risk of cavities
Monitoring and basic dental care usually prevent complications.
Recommended Treatment Process
Initial Assessment (Days 1–3)
-
Dental examination
-
Assessment of tooth eruption stage
-
Evaluation of gum hygiene
Active Care Phase (Days 4–7)
Treatment may include:
-
Professional cleaning if plaque is present
-
Oral hygiene instruction for child and parent
-
Mild antiseptic rinse if recommended
Healing and Observation Phase (Days 8–14)
-
Swelling should gradually reduce
-
Gums return to a healthier color
-
Comfort improves
Most cases resolve without invasive treatment.
Expected Healing Time
-
Mild swelling: 3–7 days
-
Eruption-related swelling: up to 14 days
Healing depends on oral hygiene and natural tooth movement.
What Happens If Care Is Delayed
If oral care is poor, this may lead to:
-
Chronic gingivitis
-
Gum bleeding
-
Tooth sensitivity
-
Higher risk of cavities
-
Need for more frequent dental visits
Early care prevents long-term issues.
Home Care Advice
Parents and patients should:
-
Brush twice daily with a soft toothbrush
-
Use gentle circular brushing on gums
-
Avoid sugary snacks
-
Encourage rinsing after meals
Seek dental advice if swelling worsens or becomes painful.
Professional Comment
This case appears consistent with gum swelling related to eruption or mild gingival inflammation in a young patient. With proper hygiene and monitoring, outcomes are usually excellent.
Visit a Dental Clinic Near You
For pediatric gum evaluation and guidance, visit:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic