Because Every Tooth Deserves Care.
Lateral Tongue Lesion Case Analysis and Healing Timeline
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
Teeth Case – Full Analysis and Provisional Diagnosis (Zoom 100%)
Medical disclaimer:
This assessment is based solely on the provided image. A definitive diagnosis requires an in-person oral examination. Tongue lesions that persist, enlarge, or become painful must be evaluated by a licensed dental or medical professional.
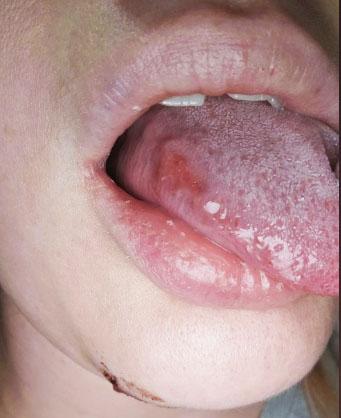
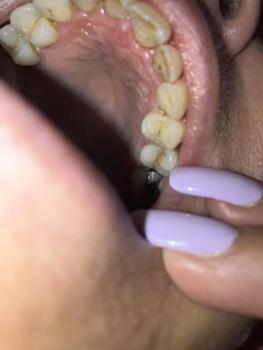
1. Visual Findings (Deep Examination)
-
Tongue (lateral/side surface):
-
Irregular reddish inflamed area with scattered white patches on the lateral border.
-
Appearance suggests surface irritation with secondary coating, not a thick fixed plaque.
-
-
Adjacent tissues:
-
Mild redness of surrounding mucosa.
-
No obvious heavy swelling in the image.
-
-
Possible contributing factors:
-
Repeated tongue friction against teeth
-
Accidental biting
-
Fungal overgrowth in an irritated area
-
Dry mouth or recent antibiotic use
-
2. Most Likely Diagnosis (Provisional)
-
Traumatic tongue lesion with secondary inflammation
-
Possible early oral candidiasis on irritated mucosa
-
Lateral tongue irritation from mechanical trauma
3. Differential Diagnosis (If Non-Healing)
-
Aphthous ulcer (canker sore)
-
Chronic traumatic ulcer
-
Oral candidiasis (if white patches increase or spread)
-
Oral potentially malignant disorder if lesion persists beyond 14 days without improvement
4. Recommended Treatment Process
Phase 1: Immediate Management (Days 1–3)
-
Clinical oral examination to identify trauma source.
-
Smooth sharp tooth edges or restorations if present.
-
Warm saltwater rinses 2–3 times daily.
-
Avoid spicy, acidic, hot, and rough foods.
Phase 2: Healing Support (Days 4–7)
-
Maintain gentle oral hygiene.
-
Consider topical antifungal or protective gel if prescribed.
-
Avoid smoking and alcohol.
Phase 3: Re-evaluation (Days 8–14)
-
Lesion should reduce in redness, size, and discomfort.
-
If unchanged or worsening, further investigation is required.
Expected healing time:
-
Traumatic tongue lesions typically heal within 7–14 days once irritation is removed.
5. If Healing Takes 14 Days – What May Scale Up
-
Persistent ulceration and pain
-
Secondary bacterial or fungal infection
-
Difficulty eating or speaking
-
Scar formation
-
Need for biopsy to exclude serious pathology
6. Home Care Recommendations (Interim)
-
Avoid biting or rubbing the tongue against teeth.
-
Do not scrape or peel white areas.
-
Maintain hydration.
-
Eat soft, non-irritating foods.
7. Professional Commentary
Lateral tongue lesions are commonly caused by trauma but must be monitored carefully. Any lesion on the side of the tongue that does not heal within two weeks requires prompt professional assessment.
Visit Nearest Dental Clinic
Find a nearby dental clinic for proper diagnosis and management:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic