Your Smile, Perfected with Precision.
Dental Case Analysis: Severe Mandibular Bone Fracture with Tooth Involvement
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
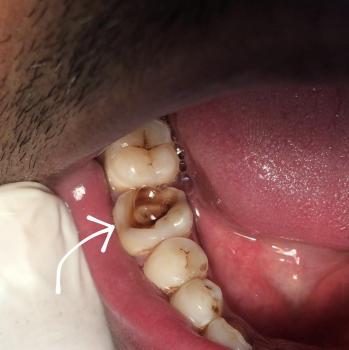
Visual Examination (Zoom 100%)
-
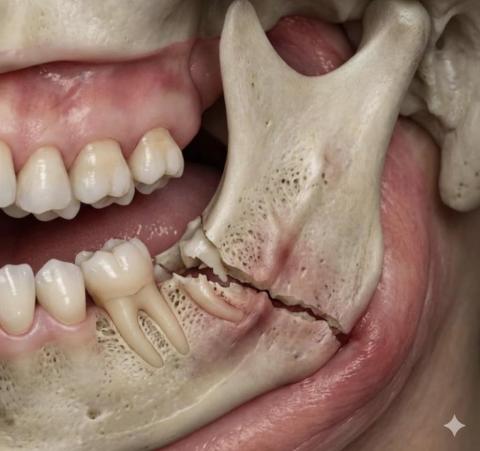
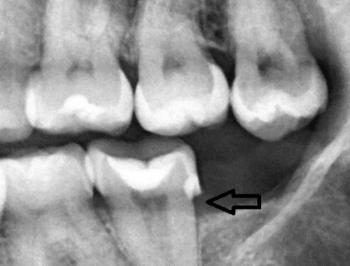
Clear fracture line across the mandibular bone (lower jaw), extending through the alveolar process
-
Discontinuity of bone structure, indicating a mandibular fracture
-
Adjacent posterior teeth involved in the fracture line
-
Visible bone porosity and cortical disruption
-
Gingival tissues appear traumatized with signs of inflammation
-
Teeth near the fracture show loss of bony support, increasing mobility risk
Primary Diagnosis
-
Mandibular fracture involving the alveolar bone
-
Dental trauma affecting posterior mandibular teeth
-
High risk of tooth instability and secondary infection
-
Possible occlusal misalignment due to fracture displacement
Contributing Causes (Possible)
-
Facial trauma or impact
-
Untreated severe periodontal disease leading to weakened bone
-
Pathologic fracture due to bone loss or infection
-
Accidental injury or bite-related stress on compromised bone
Recommended Clinical Process to Execute
-
Immediate clinical assessment
-
Panoramic X-ray (OPG) or CBCT scan
-
Evaluate fracture extent and nerve involvement
-
-
Stabilization
-
Temporary immobilization of the jaw if needed
-
-
Surgical or non-surgical management
-
Open or closed reduction depending on fracture severity
-
Possible fixation using plates or wires
-
-
Dental management
-
Evaluate fractured-area teeth for:
-
Extraction if non-restorable
-
Splinting if salvageable
-
-
-
Medication
-
Antibiotics to prevent infection
-
Pain management and anti-inflammatory drugs
-
-
Soft diet and strict oral hygiene
-
Close monitoring and follow-up
Estimated Time Frame to Heal
-
Initial healing phase: 2–4 weeks
-
Bone consolidation: 6–8 weeks
-
Full functional recovery: 8–12 weeks
If intervention starts within 14 days, prognosis improves significantly, especially for bone union and infection control.
If Left Untreated or Delayed
Issues that may scale up include:
-
Chronic infection or osteomyelitis
-
Permanent tooth loss
-
Worsening jaw misalignment
-
Persistent pain and swelling
-
Nerve damage leading to numbness
-
Compromised chewing and speech
-
More complex and costly surgery later
Professional Comments
This case requires urgent dental and maxillofacial evaluation. Jaw fractures involving teeth should never be ignored, as delayed care increases complications and recovery time. Early diagnosis and intervention are critical for preserving both bone structure and remaining teeth.
Next Step for Patients
Visit the nearest dental or maxillofacial clinic for immediate evaluation.
You may search for a nearby dental clinic using our directory: