We Bring Back the Sparkle in Your Smile.
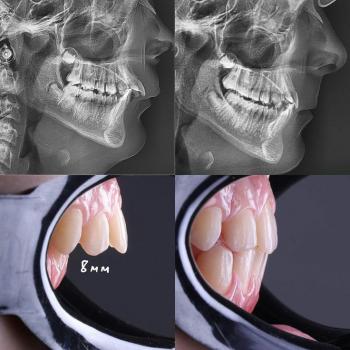
Interproximal Cavity and Gum Irritation in Premolar - Zoomed Dental Case Analysis
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
Teeth Case – Zoom 100%
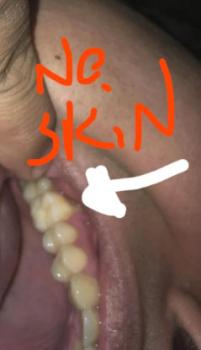
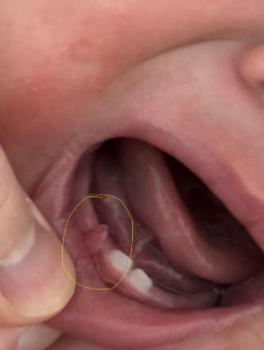
Focused Area: Upper posterior teeth (premolar region) with circled interproximal defect near the gumline
Full Analysis and Deep Visual Examination
This assessment is based on the provided image only and does not replace a comprehensive dental examination, bitewing X-rays, or periodontal probing.
Observed Findings
-
Visible structural defect on the circled tooth consistent with an interproximal cavity and/or fractured enamel
-
Plaque-retentive margin at the cervical (neck) area of the tooth
-
Localized gingival irritation adjacent to the defect
-
Irregular contact point that traps food and bacteria
-
Tooth surface discoloration suggesting active decay rather than stain
Probable Diagnosis
-
Interproximal dental caries (moderate to advanced)
-
Possible enamel fracture with secondary decay
-
Localized plaque-induced gingivitis
-
Risk of pulp involvement depending on cavity depth (X-ray required)
Recommended Treatment Process
Step 1: Full Mouth Scaling and Polishing (Day 1)
-
Ultrasonic scaling to remove plaque and calculus
-
Manual scaling around the affected contact area
-
Polishing to reduce bacterial re-adhesion
Estimated duration: 30–60 minutes
Local anesthesia: May be required due to sensitivity near the lesion
Step 2: Definitive Tooth Repair (Day 1–7)
Treatment choice depends on depth and structure:
-
Composite filling if decay is confined to enamel/dentin
-
Onlay or crown if significant tooth structure is lost
-
Root canal treatment if pulp exposure or infection is confirmed
Healing and Recovery Timeline
| Time Frame | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Days 1–3 | Gum tenderness and irritation reduce |
| Days 4–7 | Gingival tissue stabilizes |
| Days 8–14 | Healthy gum contour if defect is properly restored |
A 14-day healing period is realistic for gum tissue once the cavity is sealed.
What Will Scale Up If Left Untreated
-
Enlargement of the cavity into deeper dentin and pulp
-
Persistent food impaction and bad breath
-
Increased gum inflammation and pocket formation
-
Development of tooth abscess or infection
-
Eventual tooth fracture or tooth loss
-
More invasive and costly treatment later
Post-Treatment Care Instructions
-
Brush twice daily with a soft-bristle toothbrush
-
Floss daily, especially between the affected teeth
-
Use fluoride toothpaste; consider high-fluoride products if advised
-
Avoid chewing hard foods on the treated side until restored
-
Reduce sugar and acidic food intake
Professional Comment
This case represents a high-risk interproximal lesion. Scaling alone will not stop progression. Prompt restoration of the tooth surface is essential to protect the gum and prevent deeper infection.
Visit a Dental Clinic Near You
For scaling, X-rays, and definitive cavity treatment, find a nearby clinic using our directory: