Your Smile, Perfected with Precision.
Severe Oral Abscess With Active Bleeding Case Analysis
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
Severe Oral Abscess With Active Bleeding Case Analysis
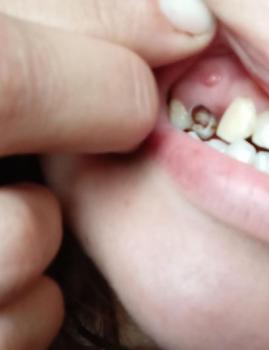
What Is Seen in This Case
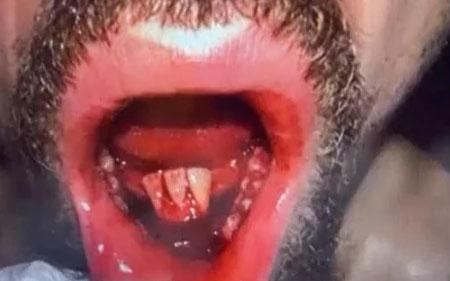
The image shows a severe open oral wound with heavy redness, exposed tissue, and active bleeding inside the mouth. The affected area appears to involve the lower front teeth region, with significant tissue damage and infection. The surrounding lips and oral tissue are highly inflamed.
This presentation indicates a serious and advanced oral infection, likely involving both soft tissue and underlying structures.
Most Likely Diagnosis
Based on visual examination, the most likely conditions include:
-
Severe dental or periodontal abscess
-
Advanced oral soft tissue infection
-
Possible necrotic (dying) tissue
-
Infection involving tooth roots and surrounding bone
-
High risk of systemic infection
This is not a mild dental problem and requires urgent professional care.
What Causes This Level of Infection
Common contributing factors include:
-
Untreated tooth abscess
-
Long-standing severe tooth decay
-
Gum disease left untreated
-
Trauma to infected teeth
-
Delayed or avoided dental care
Once infection reaches this stage, it can spread rapidly.
Is This a Medical Emergency
Yes. This condition is urgent.
If untreated, it may scale up into:
-
Rapid spread of infection to jawbone
-
Facial or neck swelling
-
Fever and systemic infection (sepsis)
-
Difficulty breathing or swallowing
-
Hospital admission
Immediate dental or medical evaluation is critical.
Recommended Treatment Process
Emergency Assessment (Same Day)
-
Urgent dental or hospital evaluation
-
Pain control and bleeding management
-
Imaging to assess bone and tooth involvement
Active Infection Control (Days 1–7)
Treatment may include:
-
Surgical drainage of abscess
-
Removal of severely infected teeth
-
Antibiotic therapy
-
Cleaning of necrotic tissue
Healing and Monitoring Phase (Days 8–14)
-
Reduction in swelling and bleeding
-
Gradual tissue healing
-
Follow-up visits to prevent recurrence
Long-term reconstruction may be needed after infection control.
Expected Healing Time
-
Acute pain relief: 2–4 days after treatment
-
Soft tissue healing: 7–14 days
-
Bone recovery may take longer depending on damage
Early treatment improves outcomes significantly.
What Happens If Treatment Is Delayed
Delaying care can result in:
-
Life-threatening infection
-
Permanent tissue damage
-
Tooth and bone loss
-
Emergency hospitalization
-
Increased treatment cost and complexity
This condition should never be ignored.
What to Do Immediately
-
Seek emergency dental or hospital care
-
Do not attempt home remedies
-
Do not press or drain the area yourself
-
Avoid smoking, alcohol, or irritating foods
Professional Comment
This case represents a severe oral abscess with active bleeding and tissue destruction. Immediate intervention is required to control infection and protect the patient’s overall health. Early treatment can be lifesaving.
Visit a Dental Clinic or Emergency Facility Near You
For urgent dental infection care, find help immediately at:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic