Smile Again with Comfort and Confidence.
Large Red Gum Swelling Near Tooth - Dental Case Analysis
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
Dental Case Analysis – Large Red Gum Swelling Near Posterior Tooth
Case Overview
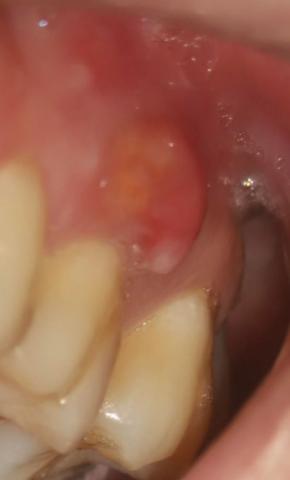
This intra-oral image shows a large, red, swollen lesion on the gum tissue adjacent to a posterior tooth. The appearance is consistent with an active localized gum infection, likely involving deeper periodontal tissues and possibly the underlying bone if not treated promptly.
Full Analysis and Diagnosis
Clinical Findings
-
Prominent red, dome-shaped swelling on gingiva
-
Inflamed, shiny soft tissue
-
Localized tenderness likely present
-
Adjacent tooth shows plaque accumulation near the gum margin
-
No visible drainage at the time of imaging
Infection Characteristics
-
Acute inflammatory response
-
Likely accumulation of bacteria beneath the gum
-
Pressure buildup within soft tissue
-
High risk of abscess formation
Diagnosis
-
Localized gingival or periodontal abscess
-
Acute gum infection adjacent to posterior tooth
-
Possible early spread toward supporting bone
Deep Clinical Examination
Tissue Assessment
-
Severe inflammation of gingival tissue
-
Possible pus accumulation beneath surface
-
Compromised blood flow due to swelling
-
Tissue breakdown risk if untreated
Possible Causes
-
Deep periodontal pocket
-
Trapped food debris
-
Untreated periodontal disease
-
Cracked or infected tooth beneath the gum
Time Frame to Heal
With Proper Treatment
-
Infection control: 3–7 days
-
Swelling reduction: 5–10 days
-
Gum tissue recovery: 1–2 weeks
-
Full stabilization: 2–4 weeks
Without Treatment
-
Rapid abscess enlargement
-
Severe pain and pressure
-
Spread of infection to jawbone
-
Facial swelling
-
Emergency dental intervention required
Process to Execute (14-Day Window)
Days 1–3
-
Immediate clinical examination
-
Drainage if abscess is present
-
Local cleaning and irrigation
-
Antibiotics only if clinically indicated
Days 4–7
-
Address underlying cause (periodontal treatment or tooth therapy)
-
Reduce bacterial load
-
Monitor swelling and pain
Days 8–14
-
Re-evaluation of gum healing
-
Confirm infection resolution
-
Plan long-term periodontal maintenance
Issues That Will Scale Up If Untreated
-
Abscess rupture
-
Jawbone infection
-
Tooth mobility or loss
-
Facial cellulitis
-
Systemic infection risk
-
Increased treatment complexity
Clinical Comments
Large red gum swellings are not normal and usually indicate an active infection under pressure. These conditions rarely resolve on their own. Early professional care prevents serious complications and protects surrounding bone and teeth.
Find a Dental Clinic Near You
Use our directory to locate a dental clinic in your area:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic