Where Bright Smiles Begin.
Gum Growth Near Back Tooth: Causes, Treatment, and Healing Timeline
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
What Is Seen in This Case?
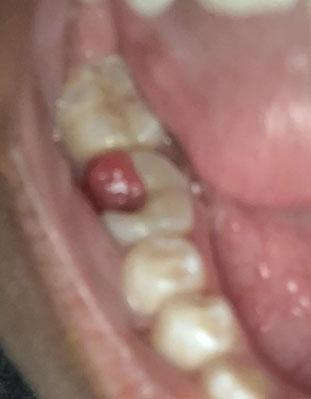
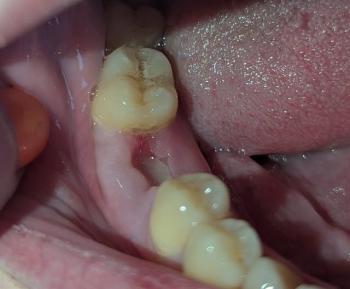
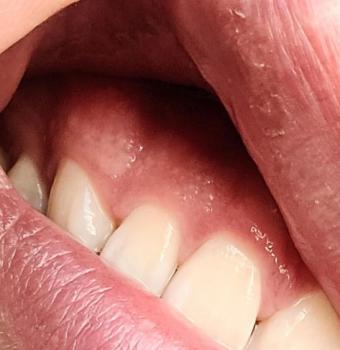
The image shows a red, swollen growth on the gum near a back tooth (molar). The surrounding tooth appears intact, but the gum tissue is inflamed and raised. This type of lesion is commonly associated with local infection, irritation, or gum overgrowth.
This condition should not be ignored, even if pain is mild.
Most Likely Diagnosis
Based on visual examination, the most likely conditions include:
-
Localized gum infection
-
Gingival abscess
-
Inflammatory gum growth (hyperplasia)
-
Irritation caused by trapped food or plaque
-
Reaction to decay or infection under the gum
A dental examination and X-ray are needed to confirm the exact cause.
What Causes This Type of Gum Problem?
Common causes include:
-
Food debris stuck between teeth
-
Plaque and tartar buildup
-
Untreated tooth decay
-
Gum trauma from chewing
-
Bacterial infection below the gumline
When bacteria are trapped, the gum may swell and form a red lump.
Is This a Serious Condition?
At an early stage, this problem is treatable and manageable. However, if left untreated, it can worsen and lead to:
-
Increased pain and swelling
-
Pus formation (abscess)
-
Spread of infection to nearby tissues
-
Damage to the tooth or bone
-
Tooth loss in severe cases
Recommended Treatment Process
Step 1: Dental Examination (Days 1–3)
-
Clinical evaluation of the gum growth
-
Dental X-ray to check for hidden infection
-
Identification of the infection source
Step 2: Active Treatment (Days 4–7)
Depending on the cause, treatment may include:
-
Professional cleaning and drainage
-
Removal of trapped debris
-
Antibiotics if infection is present
-
Treatment of the affected tooth if needed
Step 3: Healing and Review (Days 8–14)
-
Swelling should gradually reduce
-
Gum tissue should return closer to normal color
-
Pain and discomfort should resolve
If the lump does not shrink, further treatment may be required.
Expected Healing Time
-
Mild gum infection: 7–10 days
-
Moderate infection: up to 14 days with treatment
Healing depends on early intervention and proper oral care.
What Happens If Treatment Is Delayed?
If ignored for more than 14 days, this condition may lead to:
-
Worsening infection
-
Formation of a dental abscess
-
Jawbone involvement
-
Fever or facial swelling
-
Higher treatment cost later
Early care prevents complications.
What You Can Do at Home (Temporary Only)
These steps do not replace dental treatment, but may reduce irritation:
-
Rinse gently with warm salt water
-
Avoid chewing on the affected side
-
Maintain gentle brushing
-
Do not press or attempt to pop the swelling
Seek dental care as soon as possible.
Professional Comment
A red gum lump near a tooth is often a warning sign of infection. Early dental treatment is simpler, safer, and more affordable than delayed care. Prompt evaluation protects both the gums and the tooth.