We Bring Back the Sparkle in Your Smile.
Posterior Tooth Decay Case Analysis and Treatment Guide
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
Dental Case Analysis: Posterior Tooth Decay and Restoration Risk
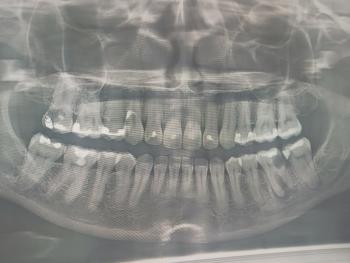
Case Overview (100% Zoom Visual Inspection)
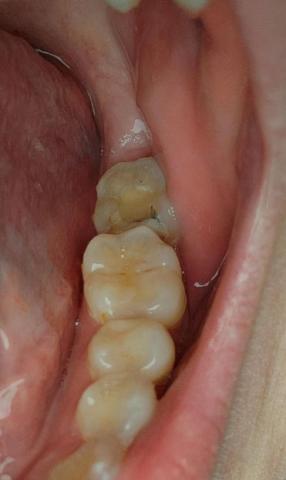
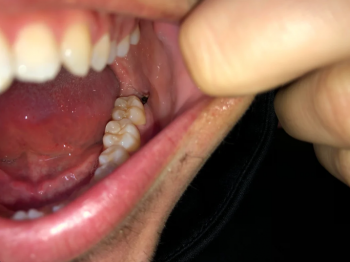
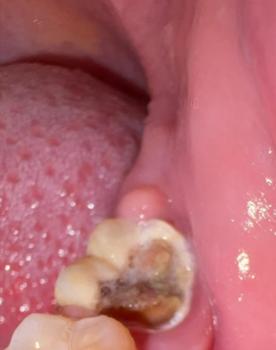
The image shows posterior molars/premolars with visible occlusal surface discoloration, dark pits, and irregular enamel texture. One tooth presents brown-black staining within fissures, strongly suggestive of active dental caries or recurrent decay under an old restoration.
Tooth-by-Tooth Visual Assessment
Tooth 1 (Most Posterior Visible)
-
Dark fissure staining
-
Loss of natural enamel translucency
-
Possible early cavitation
-
High plaque retention area
Tooth 2 (Middle Molar)
-
Yellow-brown occlusal discoloration
-
Surface wear and staining
-
Early enamel demineralization suspected
Tooth 3 (Anterior Premolar)
-
Mild staining
-
Enamel largely intact
-
Lower immediate risk
Clinical Diagnosis (Visual-Based)
-
Primary diagnosis: Occlusal dental caries
-
Secondary concern: Enamel demineralization
-
Risk of progression to dentin involvement
-
Possible microleakage if an old filling exists
Deep Examination Findings
-
Caries likely confined to enamel → early dentin stage
-
No visible fracture lines
-
No obvious abscess or gum swelling
-
Tongue-side moisture suggests normal salivary flow
Recommended Treatment Process
Step 1: Clinical Confirmation (Day 1)
-
Bitewing X-ray
-
Cold sensitivity test
-
Caries detection dye (if needed)
Step 2: Conservative Restoration (Day 1–3)
-
Caries removal
-
Composite resin filling
-
Occlusal sealant if early lesion
Step 3: Post-Treatment Care (Day 3–14)
-
Fluoride toothpaste (high-fluoride if prescribed)
-
Avoid hard or sticky foods
-
Maintain oral hygiene
Expected Healing Time Frame
-
Soft tissue recovery: 24–72 hours
-
Tooth sensitivity resolution: 7–14 days
-
Full functional comfort: within 14 days
If Treatment Is Delayed Beyond 14 Days
The following issues may scale up:
-
Caries progression into dentin
-
Increased pain and sensitivity
-
Risk of pulp inflammation
-
Possible need for root canal treatment
-
Higher treatment cost and time
Professional Comments
Early intervention allows simple, low-cost restoration. Delay may lead to irreversible pulp damage. Posterior teeth are high-risk due to deep fissures and chewing pressure.
Find a Nearby Dental Clinic
Visit your nearest clinic using our directory:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic