Your Smile, Our Passion.
Full Mouth Dental Infection Seen on Panoramic X-Ray - Case Analysis
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
Dental Case Analysis – Full Mouth Panoramic X-Ray With Multiple Infection Sites
Case Overview
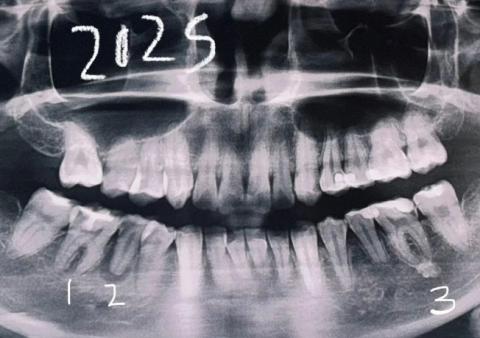
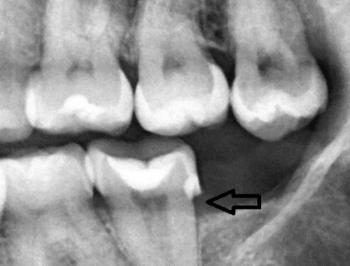
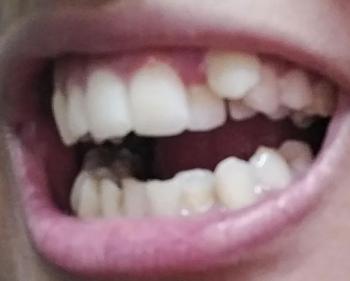
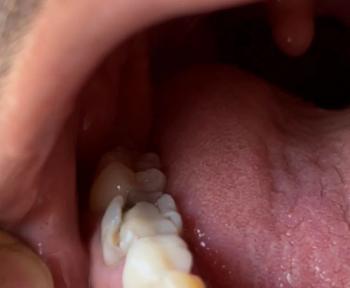
This panoramic dental X-ray shows a full-mouth view of the maxilla and mandible. Several teeth demonstrate radiographic signs of infection, bone loss, and previous dental treatment. The findings suggest chronic, multi-site dental pathology rather than a single isolated issue.
Full Analysis and Diagnosis
General Radiographic Findings
-
Multiple teeth with widened periodontal ligament spaces
-
Areas of reduced bone density around root apices
-
Irregular alveolar bone levels
-
Signs consistent with chronic inflammation
-
Mixed dental history including untreated, treated, and compromised teeth
Upper Jaw Findings
-
Possible apical radiolucencies on posterior teeth
-
Early to moderate bone loss
-
Sinus floor appears intact but close to root apices
-
Risk of sinus involvement if infections progress
Lower Jaw Findings
-
Noticeable bone loss around posterior molars
-
Possible chronic apical infections
-
Increased risk to mandibular nerve if lesions enlarge
-
Structural bone thinning in affected areas
Diagnosis
-
Chronic apical periodontitis affecting multiple teeth
-
Generalized dental infection with localized bone loss
-
Long-standing inflammatory dental condition
Deep Clinical Examination
Infection Pattern
-
Chronic rather than acute presentation
-
Multiple low-grade infection sources
-
Likely developed over years
-
May exist with minimal pain symptoms
Structural Impact
-
Progressive alveolar bone loss
-
Compromised tooth support
-
Increased risk of tooth mobility
-
Reduced success rate for future implants if untreated
Time Frame to Heal
With Proper Treatment
-
Initial infection control: 7–14 days
-
Inflammation reduction: 2–3 weeks
-
Bone healing begins: 4–8 weeks
-
Radiographic improvement: 3–6 months
-
Full-mouth stabilization: 6–12 months (staged care)
Without Treatment
-
Continued bone destruction
-
Spread of infection
-
Tooth loss
-
Jawbone weakening
-
Increased need for surgical intervention
Process to Execute (14-Day Focus)
Days 1–3
-
Comprehensive clinical examination
-
Full-mouth treatment planning
-
Identify priority infection sites
-
CBCT scans for high-risk areas if needed
Days 4–7
-
Begin infection control (root canal therapy, retreatment, or extraction)
-
Periodontal debridement
-
Antibiotics only if clinically indicated
Days 8–14
-
Re-evaluation of treated areas
-
Pain and inflammation assessment
-
Plan staged continuation of care
Issues That Will Scale Up If Untreated
-
Worsening bone loss
-
Multiple tooth failures
-
Chronic abscess formation
-
Facial swelling
-
Sinus or nerve involvement
-
Reduced eligibility for implants
-
Long-term oral health decline
Clinical Comments
Panoramic X-rays often reveal hidden, silent infections that are not yet symptomatic. Early intervention and staged treatment planning are critical to preserve remaining bone and teeth. Full-mouth cases require coordinated, long-term care.
Find a Dental Clinic Near You
Search for a qualified dental clinic using our directory:
https://cebudentalimplants.com/map-dental-clinic