Missing Teeth? Find Your Smile Again.
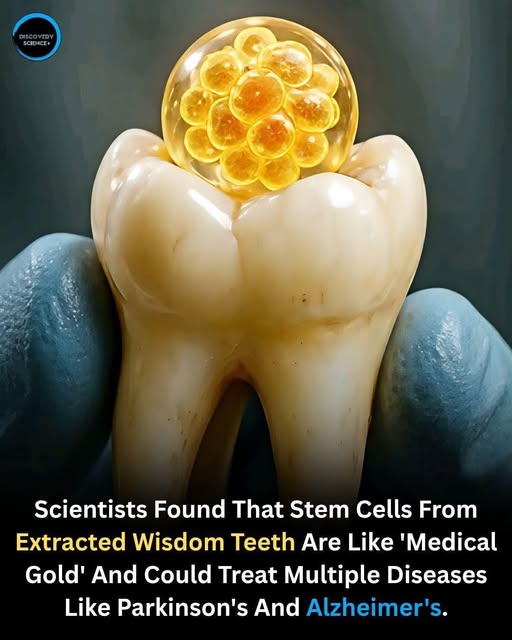
The Surprising Medical Value of Wisdom Teeth: Unlocking Future Cures
Language :
Topics:
Beyond Removal: Why Your Wisdom Teeth Could Be a Medical Treasure
For generations, wisdom teeth have been synonymous with one thing: extraction. Viewed as vestigial troublemakers, they’re often removed at the first sign of crowding or discomfort and unceremoniously discarded. But what if we’ve been throwing away a biological goldmine? Groundbreaking scientific research is now revealing that these often-discarded molars hold an extraordinary secret—a potent source of stem cells with the potential to revolutionize the future of medicine.
The Hidden Power Within: Dental Stem Cells
Scientists have discovered that the dental pulp inside wisdom teeth is rich in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). But these aren’t just any stem cells. Research indicates they are incredibly potent, highly proliferative, and, most importantly, possess a remarkable ability to differentiate into neurons and other neural cells.
This opens a breathtaking frontier: the possibility of using a patient’s own wisdom teeth to develop treatments for some of our most challenging neurological disorders, including:
-
Parkinson’s Disease
-
Alzheimer’s Disease
-
Spinal Cord Injuries
-
Stroke Recovery
Why Wisdom Tooth Stem Cells Are So Special
-
Neural Crest Origin: Wisdom teeth stem cells originate from the neural crest during embryonic development—the same tissue that gives rise to the brain and peripheral nervous system. This gives them a natural "pre-programming" and affinity for becoming nervous system cells, making them uniquely suited for neurological therapies.
-
Accessibility & Potency: Compared to harvesting stem cells from bone marrow, extracting them from a removed wisdom tooth is minimally invasive, low-risk, and painless (the tooth is already coming out!). Furthermore, these dental stem cells are young, highly active, and have shown strong regenerative capabilities in laboratory studies.
-
Immunological Safety: Using your own cells (autologous transplant) vastly reduces the risk of immune rejection, a significant hurdle in other stem cell therapies.
The Science in Action: From Lab to Future Therapy
Laboratory studies have already demonstrated compelling success. Dental stem cells have been shown to:
-
Secrete neuroprotective factors that support damaged brain cells.
-
Differentiate into functional neurons in culture.
-
Promote nerve regeneration and repair in models of spinal injury.
The pathway is clear: researchers are actively working on methods to harvest, bank, and program these cells to repair specific neural damage.
A Paradigm Shift: From Discarding to Preserving
This research prompts a profound shift in perspective. The routine dental procedure of wisdom tooth removal is transformed from an endpoint into a potential biomedical opportunity.
The next time your dentist discusses extraction, you might consider a new question: Should we preserve the stem cells?
Dental Stem Cell Banking is an emerging field where the living pulp tissue is carefully collected after removal, processed, and cryogenically frozen for potential future use. It’s an insurance policy written in your own biology.
The Future at the Intersection of Dentistry and Medicine
We are standing at the convergence of dentistry and regenerative medicine. The message is clear: Your wisdom teeth might be more valuable than you think. They are not merely evolutionary leftovers but a possibly accessible, personal reservoir of healing potential.
While widespread clinical therapies are still on the horizon, the discovery underscores the incredible complexity and value of the human body—even in its seemingly unnecessary parts. It encourages a dialogue between patient and dentist that looks beyond immediate dental health to consider lifelong biological resources.
Final Thought: In the future, saving your wisdom teeth’s stem cells could be as commonplace as saving baby teeth. What was once considered a dental burden may one day become a key to unlocking treatments for conditions that affect millions, turning a routine procedure into an act of profound medical foresight.