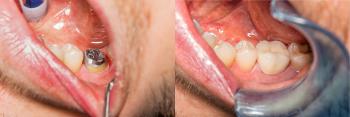
Missing Teeth? Find Your Smile Again.
Severe tooth decay treatment Philippines
Severity:
Teeth Problems:
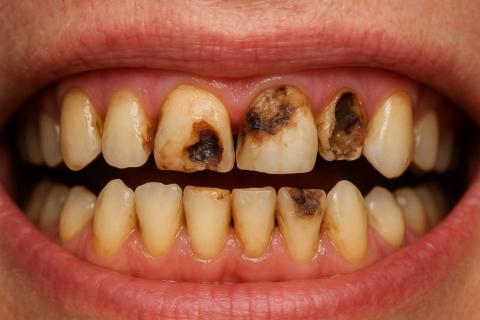
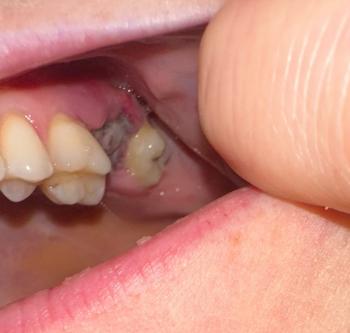
Case Analysis: Advanced Dental Caries and Enamel Erosion
Clinical Observation
Upon visual examination of the image:
-
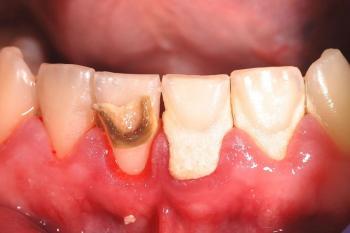
Multiple anterior teeth (upper and lower) show extensive decay, with large carious lesions exposing dentin and pulp in some areas.
-
Severe enamel erosion and discoloration are evident.
-
Possible infection or necrosis in the pulp chambers (blackened centers).
-
Gum margins appear slightly inflamed, indicating early gingivitis.
-
The tooth structure is weakened, risking fracture or complete tooth loss if untreated.
Diagnosis
Primary Diagnosis:
-
Severe dental caries (multi-surface lesions) affecting both anterior and posterior teeth.
Secondary Conditions:
-
Pulpitis or necrotic pulp (due to deep decay).
-
Enamel erosion and demineralization (from acid exposure or poor hygiene).
-
Early gum disease (gingivitis).
-
Possible malodor (halitosis) due to bacterial infection.
Probable Causes
Based on your provided list, the most relevant causes for this case include:
-
Poor Oral Hygiene:
Failure to brush and floss allowed plaque and bacteria to destroy enamel and dentin. -
Dietary Habits:
Regular intake of sugary or acidic foods and beverages accelerated decay. -
Lifestyle Factors:
Possible smoking, alcohol use, or neglect of dental visits. -
Medical Conditions:
Potential dry mouth or acid reflux contributing to enamel loss.
Treatment Plan
1. Immediate Actions
-
Dental X-rays: To assess the depth of decay and check for root or bone involvement.
-
Oral Debridement: Deep cleaning to remove plaque, tartar, and bacteria.
-
Caries Excavation: Removal of decayed portions of each affected tooth.
2. Restorative Procedures
Depending on the severity of each tooth:
| Condition | Recommended Treatment |
|---|---|
| Shallow decay | Tooth-colored composite filling |
| Deep decay but with healthy roots | Root canal treatment (RCT) + Crown restoration |
| Severely decayed beyond repair | Extraction followed by Dental implant or bridge |
3. Cosmetic and Functional Rehabilitation
Once infection is controlled and structure stabilized:
-
Porcelain crowns or veneers for aesthetic restoration.
-
Teeth whitening (only after infection-free recovery).
-
Orthodontic consultation if spacing or alignment is affected.
4. Maintenance and Prevention
-
Brush 2–3 times daily with fluoride toothpaste.
-
Floss and use mouthwash daily.
-
Limit sugary snacks and acidic drinks.
-
Regular dental check-ups every 6 months.
-
Drink more water to maintain saliva production.
-
Quit smoking and avoid alcohol.
Estimated Timeline
| Phase | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cleaning & Assessment | 1–2 visits | Scaling, polishing, X-rays |
| Decay Removal & Fillings | 2–4 visits | Depending on tooth count |
| Root Canal & Crown Work | 3–6 weeks | Healing between procedures |
| Full Rehabilitation | 1–2 months | Cosmetic and implant phases |
| Maintenance | Lifelong | Consistent hygiene & check-ups |
Expert Advice
If untreated, this level of decay can lead to abscesses, bone loss, and systemic infection. Visit your nearest dental specialist or implant center immediately. Early intervention can save most of these teeth and restore full function and confidence.